Abstract
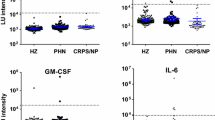
Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a severe sequela of herpes zoster (HZ). Until now, only age and pain severity were considered predisposing factors for the development of PHN. We evaluated 49 patients with acute phase HZ, 10 of whom developed PHN (Group A) and 39 of whom did not develop PHN (Group B). Twenty-five healthy volunteers similar in age and gender distribution to the study group were recruited as controls (Group C). Numbers of serum CD3+ (pan-T lymphocytes), CD4+ (helper/inducer), and CD8+ (suppressor/cytotoxic) lymphocytes were decreased significantly in Groups A and B relative to the control group, but there were no statistical differences between Groups A and B. Interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, IL-8, and IL-10 were significantly elevated in Groups A and B relative to Group C. IL-6 was significantly higher in Group A than in Group B, and was significantly positively correlated with pain severity scored on a visual analog scale. Therefore, we suggest that the inflammatory response, especially that of IL-6, in the acute phase of HZ may be associated with hyperalgesia and the development of PHN.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abendroth, A., Arvin, A.M., 2001. Immune evasion as a pathogenic mechanism of varicella zoster virus. Semin. Immunol., 13(1):27–39. [doi:10.1006/smim.2001.0293]
Arruda, J.L., Sweitzer, S., Rutkowski, M.D., DeLeo, J.A., 2000. Intrathecal anti-IL-6 antibody and IgG attenuates peripheral nerve injury-induced mechanical allodynia in the rat: possible immune modulation in neuropathic pain. Brain Res., 879(1–2):216–225. [doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(00)02807-9]
Asanuma, H., Sharp, M., Maecker, H.T., Maino, V.C., Arvin, A.M., 2000. Frequencies of memory T cells specific for varicella-zoster virus, herpes simplex virus, and cytomegalovirus by intracellular detection of cytokine expression. J. Infect. Dis., 181(3):859–866. [doi:10.1086/315347]
Cauda, R., Grossi, C.E., Whitley, R.J., Tilden, A.B., 1987. Analysis of immune function in herpes zoster patients: demonstration and characterization of suppressor cells. J. Immunol., 138(4):1229–1233.
Davis, A.J., Perkins, M.N., 1996. Substance P and capsaicin-induced mechanical hyperalgesia in the rat knee joint: the involvement of bradykinin B1 and B2 receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol., 118(8):2206–2212.
Decroix, J., Partsch, H., Gonzalez, R., Mobacken, H., Goh, C.L., Walsh, L., Shukla, S., Naisbett, B., 2000. Factors influencing pain outcome in herpes zoster: an observational study with valaciclovir. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol., 14(1):23–33. [doi:10.1046/j.1468-3083.2000.00020.x]
Domingo, P., Torres, O.H., Ris, J., Vazquez, G., 2001. Herpes zoster as an immune reconstitution disease after initiation of combination antiretroviral therapy in patients with human immunodeficiency virus type-1 infection. Am. J. Med., 110(8):605–609. [doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(01)00703-3]
Donahue, J.G., Choo, P.W., Manson, J.E., Platt, R., 1995. The incidence of herpes zoster. Arch. Intern. Med., 155(15):1605–1609. [doi:10.1001/archinte.155.15.1605]
Galil, K., Choo, P.W., Donahue, J.G., Platt, R., 1997. The sequelae of herpes zoster. Arch. Intern. Med., 157(11): 1209–1213. [doi:10.1001/archinte.157.11.1209]
Helgason, S., Petursson, G., Gudmundsson, S., Sigurdsson, J.A., 2000. Prevalence of postherpetic neuralgia after a first episode of herpes zoster: prospective study with long term follow up. BMJ, 321(7264):794–796. [doi:10.1136/bmj.321.7264.794]
Higa, K., Noda, B., Manabe, H., Sato, S., Dan, K., 1992. T-lymphocyte subsets in otherwise healthy patients with herpes zoster and relationships to the duration of acute herpetic pain. Pain, 51(1):111–118. [doi:10.1016/0304-3959(92)90015-4]
Jenkins, D.E., Redman, R.L., Meng Lam, E., Liu, C., Lin, I., Arvin, A.M., 1998. Interleukin (IL)-10, IL-12, and interferon-g production in primary and memory immune responses to varicella-zoster virus. J. Infect. Dis., 178(4): 940–948. [doi:10.1086/515702]
Kost, R.G., Straus, S.E., 1996. Postherpetic neuralgia: pathogenesis, treatment and prevention. N. Engl. J. Med., 335(1):32–42. [doi:10.1056/NEJM199607043350107]
Kotani, N., Kudo, R., Sakurai, Y., Sawamura, D., Sessler, D.I., Okada, H., Nakayama, H., Yamagata, T., Yasujima, M., Matsuki, A., 2004. Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin 8 concentrations and the subsequent development of postherpetic neuralgia. Am. J. Med., 116(5):318–324. [doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2003.10.027]
Laughlin, T.M., Bethea, J.R., Yezierski, R.P., Wilcox, G.L., 2000. Cytokine involvement in dynorphin-induced allodynia. Pain, 84(2–3):159–167. [doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(99)00195-5]
Mahalingam, R., Wellish, M., Brucklier, J., Gilden, D.H., 1995. Persistence of varicella-zoster virus DNA in elderly patients with postherpetic neuralgia. J. Neurovirol., 1(1): 130–133. [doi:10.3109/13550289509111018]
Opstelten, W., Mauritz, J.W., de Wit, N.J., van Wijck, A.J., Stalman, W.A., van Essen, G.A., 2002. Herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia: incidence and risk factors using a general practice research database. Fam. Pract., 19(5): 471–475. [doi:10.1093/fampra/19.5.471]
Üçeyler, N., Tscharke, A., Sommer, C., 2007. Early cytokine expression in mouse sciatic nerve after chronic constriction nerve injury depends on calpain. Brain Behav. Immun., 21(5):553–560. [doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2006.10.003]
Vassalli, P., 1992. The pathophysiology of tumor necrosis factors. Annu. Rev. Immunol., 10(1):411–452. [doi:10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002211]
Vilcek, J., Lee, T.H., 1991. Tumor necrosis factor. New insights into the molecular mechanisms of its multiple actions. J. Biol. Chem., 266(12):7313–7316.
von Seidlein, L., Gillette, S.G., Bryson, Y., Frederick, T., Mascola, L., Church, J., Brunell, P., Kovacs, A., Deveikis, A., Keller, M., 1996. Frequent recurrence and persistence of varicella-zoster virus infections in children infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Pediatr., 128(1):52–57. [doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(96)70427-4]
Watkins, L.R., Martin, D., Ulrich, P., Tracey, K.J., Maier, S.F., 1997. Evidence for the involvement of spinal cord glia in subcutaneous formalin induced hyperalgesia in the rat. Pain, 71(3):225–235. [doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(97)03369-1]
Webster, A., Grint, P., Brenner, M.K., Prentice, H.G., Griffiths, P.D., 1989. Titration of IgG antibodies against varicella zoster virus before bone marrow transplantation is not predictive of future zoster. J. Med. Virol., 27(2):117–119. [doi:10.1002/jmv.1890270209]
Wilson, A., Sharp, M., Koropchak, C.M., Ting, S.F., Arvin, A.M., 1992. Subclinical varicella-zoster virus viremia, herpes zoster, and T lymphocyte immunity to varicella-zoster viral antigens after bone marrow transplantation. J. Infect. Dis., 165(1):119–126.
Yabuuchi, K., Maruta, E., Minami, M., Satoh, M., 1996. Induction of interleukin-1 beta mRNA in the hypothalamus following subcutaneous injections of formalin into the rat hind paws. Neurosci. Lett., 207(2):109–112. [doi:10.1016/0304-3940(96)12505-2]
Zak-Prelich, M., Mckenzie, R.C., Sysa-Jedrzejowska, A., Norval, M., 2003. Local immune responses and systemic cytokine responses in zoster: relationship to the development of postherpetic neuralgia. Clin. Exp. Immunol., 131(2):318–323. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02061.x]
Zhang, Y., Cosyns, M., Levin, M.J., Hayward, A.R., 1994. Cytokine production in varicella zoster virus-stimulated limiting dilution lymphocyte cultures. Clin. Exp. Immunol., 98(1):128–133.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. 2008ZYC07) supported by the Zhejiang Medical Bureau of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Sm., Liu, Ym., An, Ed. et al. Influence of systemic immune and cytokine responses during the acute phase of zoster on the development of postherpetic neuralgia. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 10, 625–630 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0920049
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0920049