Abstract
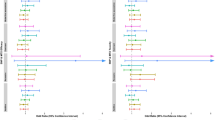
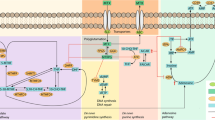
We investigated the effect of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) spanning 10 methotrexate (MTX) pathway genes, namely AMPD1, ATIC, DHFR, FPGS, GGH, ITPA, MTHFD1, SHMT1, SLC19A1 (RFC) and TYMS on the outcome of MTX treatment in a UK rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patient cohort. Tagging SNPs were selected and genotyping was performed in 309 patients with predefined outcomes to MTX treatment. Of the 129 SNPs tested, 11 associations were detected with efficacy (P-trend ⩽0.05) including four SNPs in the ATIC gene (rs12995526, rs3821353, rs7563206 and rs16853834), six SNPs in the SLC19A1 gene region (rs11702425, rs2838956, rs7499, rs2274808, rs9977268 and rs7279445) and a single SNP within the GGH gene (rs12681874). Five SNPs were significantly associated with adverse events; three in the DHFR gene (rs12517451, rs10072026, and rs1643657) and two of borderline significance in the FPGS gene. The results suggest that genetic variations in several key MTX pathway genes may influence response to MTX in the RA patients. Further studies will be required to validate these findings and if confirmed these results could contribute towards a better understanding of and ability to predict MTX response in RA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JJ, Wells G, Verhoeven AC, Felson DT . Factors predicting response to treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: the importance of disease duration. Arthritis Rheum 2000; 43: 22–29.
Finckh A, Liang MH, van Herckenrode CM, de Pablo P . Long-term impact of early treatment on radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 55: 864–872.
Weinblatt ME, Coblyn JS, Fox DA, Fraser PA, Holdsworth DE, Glass DN et al. Efficacy of low-dose methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 1985; 312: 818–822.
Williams HJ, Willkens RF, Samuelson Jr CO, Alarcon GS, Guttadauria M, Yarboro C et al. Comparison of low-dose oral pulse methotrexate and placebo in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. A controlled clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum 1985; 28: 721–730.
Le Loet X, Berthelot JM, Cantagrel A, Combe B, De Bandt M, Fautrel B et al. Clinical practice decision tree for the choice of the first disease modifying antirheumatic drug for very early rheumatoid arthritis: a 2004 proposal of the French Society of Rheumatology. Ann Rheum Dis 2006; 65: 45–50.
Sokka T, Kautiainen H, Toloza S, Makinen H, Verstappen SM, Lund Hetland M et al. QUEST-RA: quantitative clinical assessment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis seen in standard rheumatology care in 15 countries. Ann Rheum Dis 2007; 66: 1491–1496.
Jones G, Halbert J, Crotty M, Shanahan EM, Batterham M, Ahern M . The effect of treatment on radiological progression in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Rheumatology 2003; 42: 6–13.
Pincus T, Ferraccioli G, Sokka T, Larsen A, Rau R, Kushner I et al. Evidence from clinical trials and long-term observational studies that disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs slow radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis: updating a 1983 review. Rheumatology 2002; 41: 1346–1356.
Alarcon GS, Tracy IC, Blackburn Jr WD . Methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Toxic effects as the major factor in limiting long-term treatment. Arthritis Rheum 1989; 32: 671–676.
Gispen JG, Alarcon GS, Johnson JJ, Acton RT, Barger BO, Koopman WJ . Toxicity of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 1987; 14: 74–79.
Salliot C, van der Heijde D . Long-term safety of methotrexate monotherapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature research. Ann Rheum Dis 2009; 68: 1100–1104.
Chakravarty K, McDonald H, Pullar T, Taggart A, Chalmers R, Oliver S et al. BSR/BHPR guideline for disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) therapy in consultation with the British Association of Dermatologists. Rheumatology 2008; 47: 924–925.
Hoekstra M, van Ede AE, Haagsma CJ, van de Laar MA, Huizinga TW, Kruijsen MW et al. Factors associated with toxicity, final dose, and efficacy of methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2003; 62: 423–426.
Hider SL, Silman AJ, Thomson W, Lunt M, Bunn D, Symmons DP . Can clinical factors at presentation be used to predict outcome of treatment with methotrexate in patients with early inflammatory polyarthritis? Ann Rheum Dis 2009; 68: 57–62.
van Ede AE, Laan RF, Rood MJ, Huizinga TW, van de Laar MA, van Denderen CJ et al. Effect of folic or folinic acid supplementation on the toxicity and efficacy of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis: a forty-eight week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheum 2001; 44: 1515–1524.
Cronstein BN . Going with the flow: methotrexate, adenosine, and blood flow. Ann Rheum Dis 2006; 65: 421–422.
Cutolo M, Sulli A, Pizzorni C, Seriolo B, Straub RH . Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2001; 60: 729–735.
Riksen NP, Barrera P, van den Broek PH, van Riel PL, Smits P, Rongen GA . Methotrexate modulates the kinetics of adenosine in humans in vivo. Ann Rheum Dis 2006; 65: 465–470.
Jansen G, Mauritz R, Drori S, Sprecher H, Kathmann I, Bunni M et al. A structurally altered human reduced folate carrier with increased folic acid transport mediates a novel mechanism of antifolate resistance. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 30189–30198.
Laverdiere C, Chiasson S, Costea I, Moghrabi A, Krajinovic M . Polymorphism G80A in the reduced folate carrier gene and its relationship to methotrexate plasma levels and outcome of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2002; 100: 3832–3834.
McGuire JJ, Hsieh P, Bertino JR . Enzymatic synthesis of polyglutamate derivatives of 7-hydroxymethotrexate. Biochem Pharmacol 1984; 33: 1355–1361.
Hider SL, Thomson W, Mack LF, Armstrong DJ, Shadforth M, Bruce IN . Polymorphisms within the adenosine receptor 2a gene are associated with adverse events in RA patients treated with MTX. Rheumatology 2008; 47: 1156–1159.
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1988; 31: 315–324.
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ . Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 263–265.
Zhang Z, Shi Q, Sturgis EM, Spitz MR, Hong WK, Wei Q . Thymidylate synthase 5′- and 3′-untranslated region polymorphisms associated with risk and progression of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 7903–7910.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Wadelius M, Chen LY, Downes K, Ghori J, Hunt S, Eriksson N et al. Common VKORC1 and GGCX polymorphisms associated with warfarin dose. Pharmacogenomics J 2005; 5: 262–270.
Eichelbaum M, Ingelman-Sundberg M, Evans WE . Pharmacogenomics and individualized drug therapy. Annu Rev Med 2006; 57: 119–137.
Cooper GM, Johnson JA, Langaee TY, Feng H, Stanaway IB, Schwarz UI et al. A genome-wide scan for common genetic variants with a large influence on warfarin maintenance dose. Blood 2008; 112: 1022–1027.
Takeuchi F, McGinnis R, Bourgeois S, Barnes C, Eriksson N, Soranzo N et al. A genome-wide association study confirms VKORC1, CYP2C9, and CYP4F2 as principal genetic determinants of warfarin dose. PLoS Genetics 2009; 5: e1000433.
Dervieux T, Furst D, Lein DO, Capps R, Smith K, Walsh M et al. Polyglutamation of methotrexate with common polymorphisms in reduced folate carrier, aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide transformylase, and thymidylate synthase are associated with methotrexate effects in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2004; 50: 2766–2774.
Weisman MH, Furst DE, Park GS, Kremer JM, Smith KM, Wallace DJ et al. Risk genotypes in folate-dependent enzymes and their association with methotrexate-related side effects in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 607–612.
Dervieux T, Furst D, Lein DO, Capps R, Smith K, Caldwell J et al. Pharmacogenetic and metabolite measurements are associated with clinical status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate: results of a multicentred cross sectional observational study. Ann Rheum Dis 2005; 64: 1180–1185.
Sharma S, Das M, Kumar A, Marwaha V, Shankar S, Aneja R et al. Interaction of genes from influx-metabolism-efflux pathway and their influence on methotrexate efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis patients among Indians. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2008; 18: 1041–1049.
Sharma S, Das M, Kumar A, Marwaha V, Shankar S, Singh P et al. Purine biosynthetic pathway genes and methotrexate response in rheumatoid arthritis patients among north Indians. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2009; 19: 823–828.
Wessels JA, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Heijmans BT, Slagboom PE, Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, Allaart CF et al. Efficacy and toxicity of methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis are associated with single-nucleotide polymorphisms in genes coding for folate pathway enzymes. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 1087–1095.
Drozdzik M, Rudas T, Pawlik A, Gornik W, Kurzawski M, Herczynska M . Reduced folate carrier-1 80G>A polymorphism affects methotrexate treatment outcome in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacogenomics J 2007; 7: 404–407.
Hayashi H, Fujimaki C, Daimon T, Tsuboi S, Matsuyama T, Itoh K . Genetic polymorphisms in folate pathway enzymes as a possible marker for predicting the outcome of methotrexate therapy in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Pharm Ther 2009; 34: 355–361.
Takatori R, Takahashi KA, Tokunaga D, Hojo T, Fujioka M, Asano T et al. ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism influences methotrexate sensitivity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2006; 24: 546–554.
Fukino K, Kawashima T, Suzuki M, Ueno K . Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase and reduced folate carrier-1 genotypes and methotrexate serum concentrations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Toxicol Sci 2007; 32: 449–452.
Bohanec Grabar P, Logar D, Lestan B, Dolzan V . Genetic determinants of methotrexate toxicity in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a study of polymorphisms affecting methotrexate transport and folate metabolism. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2008; 64: 1057–1068.
Chatzikyriakidou A, Georgiou I, Voulgari PV, Papadopoulos CG, Tzavaras T, Drosos AA . Transcription regulatory polymorphism -43T>C in the 5′-flanking region of SLC19A1 gene could affect rheumatoid arthritis patient response to methotrexate therapy. Rheumatol Int 2007; 27: 1057–1061.
James HM, Gillis D, Hissaria P, Lester S, Somogyi AA, Cleland LG et al. Common polymorphisms in the folate pathway predict efficacy of combination regimens containing methotrexate and sulfasalazine in early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2008; 35: 562–571.
Lee YC, Cui J, Costenbader KH, Shadick NA, Weinblatt ME, Karlson EW . Investigation of candidate polymorphisms and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients on methotrexate. Rheumatology 2009; 48: 613–617.
Wessels JA, Kooloos WM, De Jonge R, De Vries-Bouwstra JK, Allaart CF, Linssen A et al. Relationship between genetic variants in the adenosine pathway and outcome of methotrexate treatment in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 2830–2839.
Hinks A, Moncrieffe H, Martin P, Ursu S, Lal S, Kassoumeri L et al. Association of the 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide transformylase gene with response to methotrexate in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70: 1395–1400.
Wessels JA, van der Kooij SM, le Cessie S, Kievit W, Barerra P, Allaart CF et al. A clinical pharmacogenetic model to predict the efficacy of methotrexate monotherapy in recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2007; 56: 1765–1775.
Dervieux T, Greenstein N, Kremer J . Pharmacogenomic and metabolic biomarkers in the folate pathway and their association with methotrexate effects during dosage escalation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 3095–3103.
van der Straaten R, Wessels JA, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, Allaart CF, Bogaartz J et al. Exploratory analysis of four polymorphisms in human GGH and FPGS genes and their effect in methotrexate-treated rheumatoid arthritis patients. Pharmacogenomics 2007; 8: 141–150.
Kato T, Hamada A, Mori S, Saito H . Genetic polymorphisms in metabolic and cellular transport pathway of methotrexate impact clinical outcome of methotrexate monotherapy in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 2011; 22 November 2011 (e-pub ahead of print).
Stamp LK, Chapman PT, O’Donnell JL, Zhang M, James J, Frampton C et al. Polymorphisms within the folate pathway predict folate concentrations but are not associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients on methotrexate. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2010; 20: 367–376.
Dervieux T, Kremer J, Lein DO, Capps R, Barham R, Meyer G et al. Contribution of common polymorphisms in reduced folate carrier and gamma-glutamylhydrolase to methotrexate polyglutamate levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacogenetics 2004; 14: 733–739.
Zeng QY, Wang YK, Xiao ZY, Chen SB . Pharmacogenetic study of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T and thymidylate synthase 3R/2R gene polymorphisms and methotrexate-related toxicity in Chinese Han patients with inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2008; 67: 1193–1194.
Ghodke Y, Chopra A, Joshi K, Patwardhan B . Are thymidylate synthase and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase genes linked with methotrexate response (efficacy, toxicity) in Indian (Asian) rheumatoid arthritis patients? Clin Rheumatol 2008; 27: 787–789.
Kumagai K, Hiyama K, Oyama T, Maeda H, Kohno N . Polymorphisms in the thymidylate synthase and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase genes and sensitivity to the low-dose methotrexate therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Med 2003; 11: 593–600.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Arthritis Research UK for their support (grant reference no 17552). SH, PM, INB, AB, WT are funded by the Arthritis Research UK and SAO's salary is funded by Pfizer. We acknowledge the NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the The Pharmacogenomics Journal website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Owen, S., Hider, S., Martin, P. et al. Genetic polymorphisms in key methotrexate pathway genes are associated with response to treatment in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Pharmacogenomics J 13, 227–234 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2012.7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2012.7
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The impact of folate pathway variants on the outcome of methotrexate therapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients
Clinical Rheumatology (2024)
-
Genetic variations in methotrexate metabolic pathway genes influence methotrexate responses in rheumatoid arthritis patients in Malaysia
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
AHR-dependent genes and response to MTX therapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2021)
-
Factors predicting addition of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs after initial methotrexate monotherapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Clinical Rheumatology (2021)
-
Folyl polyglutamate synthethase (FPGS) gene polymorphisms may influence methotrexate adverse events in South Indian Tamil Rheumatoid Arthritis patients
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2020)