Abstract
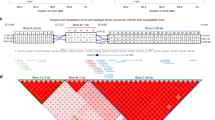
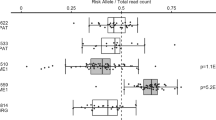
The interleukin 4 promoter polymorphism −589 C/T (rs2243250) was genotyped in 869 multiple sclerosis (MS) patients and 595 healthy blood donors. Sex-specific MS association was evident whereas two flanking polymorphisms showed insignificant P values. In dual luciferase assays of cultured Jurkat cells the cloned promoter comprising the −589 T allele leads to higher expression as compared to the respective construct with the C allele. Together these findings may be discussed functionally as contributing to the genetic predisposition and to the pathogenesis in MS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oksenberg JR, Barcellos LF . Multiple sclerosis genetics: leaving no stone unturned. Genes Immun 2005; 6: 375–387.
Hauser SL, Oksenberg JR . The neurobiology of multiple sclerosis: genes, inflammation, and neurodegeneration. Neuron 2006; 52: 61–76.
Barcellos LF, Sawcer S, Ramsay PP, Baranzini SE, Thomson G, Briggs F et al. Heterogeneity at the HLA-DRB1 locus and risk for multiple sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet 2006; 15: 2813–2824.
Opal SM, DePalo VA . Anti-inflammatory cytokines. Chest 2000; 117: 1162–1172.
Ansel KM, Djuretic I, Tanasa B, Rao A . Regulation of Th2 differentiation and Il4 locus accessibility. Annu Rev Immunol 2006; 24: 607–656.
Beghe B, Barton S, Rorke S, Peng Q, Sayers I, Gaunt T et al. Polymorphisms in the interleukin-4 and interleukin-4 receptor alpha chain genes confer susceptibility to asthma and atopy in a Caucasian population. Clin Exp Allergy 2003; 33: 1111–1117.
Vidyarani M, Selvaraj P, Prabhu Anand S, Jawahar MS, Adhilakshmi AR, Narayanan PR . Interferon gamma (IFNgamma) & interleukin-4 (IL-4) gene variants & cytokine levels in pulmonary tuberculosis. Indian J Med Res 2006; 124: 403–410.
Pawlik A, Wrzesniewska J, Florczak M, Gawronska-Szklarz B, Herczynska M . The −590 IL-4 promoter polymorphism in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 2005; 26: 48–51.
Moreno O, Gonzalez CI, Saaibi DL, Otero W, Badillo R, Martin J et al. Polymorphisms in the IL4 and IL4RA genes in Colombian patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2007; 34: 36–42.
Hosseini-Farahabadi S, Tavakkol-Afshari J, Rafatpanah H, Farid Hosseini R, Khaje Daluei M . Association between the polymorphisms of IL-4 gene promoter (−590C>T), IL-13 coding region (R130Q) and IL-16 gene promoter (−295T>C) and allergic asthma. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol 2007; 6: 9–14.
Rezazadeh M, Hajilooi M, Haidari M, Rafiei A, Alavi SA, Keramat F . Association of susceptibility to brucellosis and interleukin-4 promoter polymorphism. Scand J Infect Dis 2006; 38: 1045–1049.
Rosenwasser LJ, Klemm DJ, Dresback JK, Inamura H, Mascali JJ, Klinnert M et al. Promoter polymorphisms in the chromosome 5 gene cluster in asthma and atopy. Clin Exp Allergy 1995; 25 (Suppl 2): 7–78; discussion 95–76.
Erdfeld E, Faul F, Buchner A . GPOWER: a general power analysis program. Behav Res Methods Instr Comput 1996; 28: 1–11.
Goedde R, Sawcer S, Boehringer S, Miterski B, Sindern E, Haupts M et al. A genome screen for linkage disequilibrium in HLA-DRB1*15-positive Germans with multiple sclerosis based on 4666 microsatellite markers. Hum Genet 2002; 111: 270–277.
Goedde R, Miterski B, Drynda S, Böschow G, Oppermann J, Kekow J et al. Numerous genetic predisposition factors for rheumatic arthritis in adults and juveniles. Recent Res Devel Human Genet 2004; 2: 183–203.
Jagiello P, Klein W, Schultz H, Csernok E, Gross WL, Epplen JT . Association study of Wegener granulomatosis and the functionally relevant A645G polymorphism in the bactericidal/permeability increasing protein (BPI) gene. Int J Immunogenet 2005; 32: 3–6.
Godde R, Rohde K, Becker C, Toliat MR, Entz P, Suk A et al. Association of the HLA region with multiple sclerosis as confirmed by a genome screen using >10,000 SNPs on DNA chips. J Mol Med 2005; 83: 486–494.
Yuan HY, Chiou JJ, Tseng WH, Liu CH, Liu CK, Lin YJ et al. FASTSNP: an always up-to-date and extendable service for SNP function analysis and prioritization. Nucleic Acids Res 2006; 34: W635–W641.
Guo L, Hu-Li J, Paul WE . Probabilistic regulation of IL-4 production in Th2 cells: accessibility at the Il4 locus. Immunity 2004; 20: 193–203.
Klein-Hessling S, Schneider G, Heinfling A, Chuvpilo S, Serfling E . HMG I(Y) interferes with the DNA binding of NF-AT factors and the induction of the interleukin 4 promoter in T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 15311–15316.
Georas SN, Cumberland JE, Burke TF, Chen R, Schindler U, Casolaro V . Stat6 inhibits human interleukin-4 promoter activity in T cells. Blood 1998; 92: 4529–4538.
Li-Weber M, Giasi M, Krammer PH . Involvement of Jun and Rel proteins in up-regulation of interleukin-4 gene activity by the T cell accessory molecule CD28. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 32460–32466.
Gajewski TF, Fitch FW . Anti-proliferative effect of IFN-gamma in immune regulation. I. IFN-gamma inhibits the proliferation of Th2 but not Th1 murine helper T lymphocyte clones. J Immunol 1988; 140: 4245–4252.
Maggi E, Parronchi P, Manetti R, Simonelli C, Piccinni MP, Rugiu FS et al. Reciprocal regulatory effects of IFN-gamma and IL-4 on the in vitro development of human Th1 and Th2 clones. J Immunol 1992; 148: 2142–2147.
Glimcher LH, Murphy KM . Lineage commitment in the immune system: the T helper lymphocyte grows up. Genes Dev 2000; 14: 1693–1711.
Cantor J, Haskins K . Effector function of diabetogenic CD4 Th1 T cell clones: a central role for TNF-alpha. J Immunol 2005; 175: 7738–7745.
Ruuls SR, Hoek RM, Ngo VN, McNeil T, Lucian LA, Janatpour MJ et al. Membrane-bound TNF supports secondary lymphoid organ structure but is subservient to secreted TNF in driving autoimmune inflammation. Immunity 2001; 15: 533–543.
Nakashima H, Miyake K, Inoue Y, Shimizu S, Akahoshi M, Tanaka Y et al. Association between IL-4 genotype and IL-4 production in the Japanese population. Genes Immun 2002; 3: 107–109.
Gibson G . Population genomics: finding the variants of mass disruption. Curr Biol 2003; 13: R901–R903.
Rockman MV, Hahn MW, Soranzo N, Goldstein DB, Wray GA . Positive selection on a human-specific transcription factor binding site regulating IL4 expression. Curr Biol 2003; 13: 2118–2123.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akkad, D., Arning, L., Ibrahim, S. et al. Sex specifically associated promoter polymorphism in multiple sclerosis affects interleukin 4 expression levels. Genes Immun 8, 703–706 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364429
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364429
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association of IL-4 with pachychoroid neovasculopathy
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Interleukin 4 gene polymorphism (−589C/T) and the risk of asthma: a meta-analysis and met-regression based on 55 studies
BMC Immunology (2020)
-
Association between interleukin-4 and interleukin-10 single nucleotide polymorphisms and multiple sclerosis among Iraqi patients
Neurological Sciences (2019)
-
Polymorphic Variants of Immune Response Genes as a Risk Factor for the Development of Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2018)
-
Clinical relevance of 13 cytokine gene polymorphisms in Chinese major trauma patients
Intensive Care Medicine (2010)