Abstract
Objective: To examine prospective changes in food habits and nutrient intakes in a representative New Zealand sample of community dwelling adults aged 70 y and over.
Design: Longitudinal study with food intake data collected in 1988/89 and again in 1995/96. In an attempt to distinguish age, time and cohort effects, data were analysed longitudinally, cross-sectionally and time-sequentially.
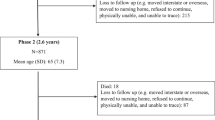
Subjects: The sample for study consisted of all non-institutionalised people aged 70 years and over registered with the Mosgiel Health Centre in 1988. In 1988/89, 678 adults completed a dietary survey (85% of those eligible) and 248 adults participated again in 1995/96 (66% of those eligible).
Results: Energy intakes declined longitudinally in men only; however, this decline appeared not to be an aging effect as energy intake was not found to decrease with age cross-sectionally. Percentage of energy from protein increased by 0.7% in women (95% confidence interval 0.2–1.2) in both the longitudinal and time-sequential analysis, suggesting a time effect. The percentage of energy from saturated fat decreased 0.7% (95% confidence interval −1.4 to −0.1) and percentage of energy from polyunsaturated fat increased 0.4% (95% confidence interval 0.0–0.7) in women, and appears to be a time effect. However, the increase in saturated fat and decrease in polyunsaturated fat with advancing age seen cross-sectionally suggests a cohort effect also occurring. In 1995/96, more people were using margarine as a spread and vegetable oils to cook meat. Milk and milk product consumption increased (not significantly), and meat intake decreased significantly by 5 and 4 servings per month in men and women, respectively. There was an increase in the proportion of people who ate breakfast cereal at least once a week, and more women ate brown or wholemeal bread in 1995/96.
Conclusion: Over the 6 y follow-up period studied, there was no indication of an age effect on nutrient intakes in adults aged 70 y and older; however, the changes occurring over time demonstrate that older adults, particularly women, are making changes towards healthier food choices.
Sponsorship: Health Research Council of New Zealand and the University of Otago Medical School.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernyhough, L., Horwath, C., Campbell, A. et al. Changes in dietary intake during a 6-year follow-up of an older population. Eur J Clin Nutr 53, 216–225 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600704
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600704
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Age-related changes in energy intake and weight in community-dwelling middle-aged and elderly Japanese
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging (2016)
-
Descriptive epidemiological study of food intake among Japanese adults: analyses by age, time and birth cohort model
BMC Public Health (2014)
-
Dietary patterns and relationship to obesity-related health outcomes and mortality in adults 75 years of age or greater
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging (2013)
-
A longitudinal study of the association between dietary factors, serum lipids, and bone marrow lesions of the knee
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2012)
-
Meat consumption and risk of primary hip and knee joint replacement due to osteoarthritis: a prospective cohort study
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2011)