Abstract
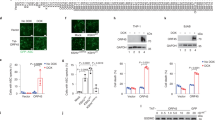
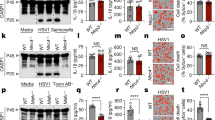
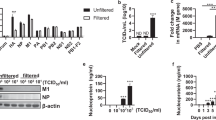
The innate immune system recognizes nucleic acids during infection and tissue damage. Whereas viral RNA is detected by endosomal toll-like receptors (TLR3, TLR7, TLR8) and cytoplasmic RIG-I and MDA5, endosomal TLR9 and cytoplasmic DAI bind DNA1, resulting in the activation of nuclear factor-κB and interferon regulatory factor transcription factors. However, viruses also trigger pro-inflammatory responses2, which remain poorly defined. Here we show that internalized adenoviral DNA induces maturation of pro-interleukin-1β in macrophages, which is dependent on NALP3 and ASC, components of the innate cytosolic molecular complex termed the inflammasome. Correspondingly, NALP3- and ASC-deficient mice display reduced innate inflammatory responses to adenovirus particles. Inflammasome activation also occurs as a result of transfected cytosolic bacterial, viral and mammalian (host) DNA, but in this case sensing is dependent on ASC but not NALP3. The DNA-sensing pro-inflammatory pathway functions independently of TLRs and interferon regulatory factors. Thus, in addition to viral and bacterial components or danger signals in general, inflammasomes sense potentially dangerous cytoplasmic DNA, strengthening their central role in innate immunity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kawai, T. & Akira, S. TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ. 13, 816–825 (2006)
Ishii, K. J. & Akira, S. Innate immune recognition of, and regulation by, DNA. Trends Immunol. 27, 525–532 (2006)
Stetson, D. B. & Medzhitov, R. Recognition of cytosolic DNA activates an IRF3-dependent innate immune response. Immunity 24, 93–103 (2006)
Takaoka, A. et al. DAI (DLM-1/ZBP1) is a cytosolic DNA sensor and an activator of innate immune response. Nature 448, 501–505 (2007)
Sergerie, Y., Rivest, S. & Boivin, G. Tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1-β play a critical role in the resistance against lethal herpes simplex virus encephalitis. J. Infect. Dis. 196, 853–860 (2007)
Kay, M. A., Glorioso, J. C. & Naldini, L. Viral vectors for gene therapy: the art of turning infectious agents into vehicles of therapeutics. Nature Med. 7, 33–40 (2001)
Muruve, D. A., Barnes, M. J., Stillman, I. E. & Libermann, T. A. Adenoviral gene therapy leads to rapid induction of multiple chemokines and acute neutrophil-dependent hepatic injury in vivo. Hum. Gene Ther. 10, 965–976 (1999)
Shayakhmetov, D. M., Li, Z. Y., Ni, S. & Lieber, A. Interference with the IL-1-signaling pathway improves the toxicity profile of systemically applied adenovirus vectors. J. Immunol. 174, 7310–7319 (2005)
Fritz, J. H., Ferrero, R. L., Philpott, D. J. & Girardin, S. E. Nod-like proteins in immunity, inflammation and disease. Nature Immunol. 7, 1250–1257 (2006)
Petrilli, V., Dostert, C., Muruve, D. A. & Tschopp, J. The inflammasome: a danger sensing complex triggering innate immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 19, 615–622 (2007)
Franchi, L. et al. Intracellular NOD-like receptors in innate immunity, infection and disease. Cell. Microbiol. 10, 1–8 (2008)
Cotter, M. J., Zaiss, A. K. & Muruve, D. A. Neutrophils interact with adenovirus vectors via Fc receptors and complement receptor 1. J. Virol. 79, 14622–14631 (2005)
Stilwell, J. L., McCarty, D. M., Negishi, A., Superfine, R. & Samulski, R. J. Development and characterization of novel empty adenovirus capsids and their impact on cellular gene expression. J. Virol. 77, 12881–12885 (2003)
Kanneganti, T. D. et al. Critical role for cryopyrin/Nalp3 in activation of caspase-1 in response to viral infection and double-stranded RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 36560–36568 (2006)
Boyden, E. D. & Dietrich, W. F. Nalp1b controls mouse macrophage susceptibility to anthrax lethal toxin. Nature Genet. 38, 240–244 (2006)
Franchi, L., Kanneganti, T. D., Dubyak, G. R. & Nunez, G. Differential requirement of P2X7 receptor and intracellular K+ for caspase-1 activation induced by intracellular and extracellular bacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 18810–18818 (2007)
Petrilli, V. et al. Activation of the NALP3 inflammasome is triggered by low intracellular potassium concentration. Cell Death Differ. 14, 1583–1589 (2007)
Henry, T., Brotcke, A., Weiss, D. S., Thompson, L. J. & Monack, D. M. Type I interferon signaling is required for activation of the inflammasome during Francisella infection. J. Exp. Med. 204, 987–994 (2007)
Zhu, J., Huang, X. & Yang, Y. Innate immune response to adenoviral vectors is mediated by both TLR-dependent and -independent pathways. J. Virol. 81, 3170–3180 (2007)
Nociari, M., Ocheretina, O., Schoggins, J. W. & Falck-Pedersen, E. Sensing infection by adenovirus: toll-like receptor-independent viral DNA recognition signals activation of the interferon regulatory factor 3 master regulator. J. Virol. 81, 4145–4157 (2007)
Fujioka, N. et al. Interleukin-18 protects mice against acute herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. J. Virol. 73, 2401–2409 (1999)
Johnston, J. B. et al. A poxvirus-encoded pyrin domain protein interacts with ASC-1 to inhibit host inflammatory and apoptotic responses to infection. Immunity 23, 587–598 (2005)
Fernandes-Alnemri, T. et al. The pyroptosome: a supramolecular assembly of ASC dimers mediating inflammatory cell death via caspase-1 activation. Cell Death Differ. 14, 1590–1604 (2007)
Sun, K. H., Yu, C. L., Tang, S. J. & Sun, G. H. Monoclonal anti-double-stranded DNA autoantibody stimulates the expression and release of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10 and TNF-α from normal human mononuclear cells involving in the lupus pathogenesis. Immunology 99, 352–360 (2000)
Jin, Y. et al. NALP1 in vitiligo-associated multiple autoimmune disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 356, 1216–1225 (2007)
Tibbles, L. A. et al. Activation of p38 and ERK signaling during adenovirus vector cell entry lead to expression of the C-X-C chemokine IP-10. J. Virol. 76, 1559–1568 (2002)
Cotten, M. et al. Psoralen treatment of adenovirus particles eliminates virus replication and transcription while maintaining the endosomolytic activity of the virus capsid. Virology 205, 254–261 (1994)
Muruve, D. A. et al. Helper-dependent adenovirus vectors elicit intact innate but attenuated adaptive host immune responses in vivo. J. Virol. 78, 5966–5972 (2004)
Mariathasan, S. et al. Differential activation of the inflammasome by caspase-1 adaptors ASC and Ipaf. Nature 430, 213–218 (2004)
Martinon, F., Petrilli, V., Mayor, A., Tardivel, A. & Tschopp, J. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature 440, 237–241 (2006)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research, operating and group grants from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, the Swiss Committee for Technology and Innovation and MUGEN. D.A.M. is the recipient of an AHFMR Scholar Award; A.K.Z. is the recipient of a Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada Studentship; V.P. is the recipient of a Marie Curie training award. We thank R. Castillo for technical assistance, V. Dixit, A. Trumpp and S. Akira for knockout mice and P. Vandenabeele for the caspase-1 antibody.
Author Contributions D.A.M., V.P., A.K.Z., L.R.W., S.A.C., P.J.R. and R.J.P. conceived the research and conducted the experiments. J.T. oversaw the whole project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
The file contains Supplementary Figures 1-10 with Legends. (PDF 5291 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muruve, D., Pétrilli, V., Zaiss, A. et al. The inflammasome recognizes cytosolic microbial and host DNA and triggers an innate immune response. Nature 452, 103–107 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06664
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06664
This article is cited by
-
Bi-Directional Relationship Between Autophagy and Inflammasomes in Neurodegenerative Disorders
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Veillonella parvula promotes the proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma through the nucleotide oligomerization domain 2/cellular communication network factor 4/nuclear factor kappa B pathway
Discover Oncology (2023)
-
cGAS inhibition alleviates Alu RNA-induced immune responses and cytotoxicity in retinal pigmented epithelium
Cell & Bioscience (2022)
-
PGC-1α inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome via preserving mitochondrial viability to protect kidney fibrosis
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Pyroptosis and pyroptosis-inducing cancer drugs
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.