Abstract
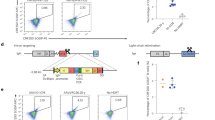
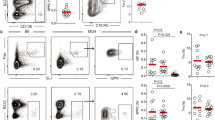
Immunoglobulin gene recombination can result in the assembly of self-reactive antibodies. Deletion, anergy or receptor editing normally silence B cells that produce these autoantibodies. Receptor editing is highly efficient in mouse B cells that carry pre-recombined autoantibody transgenes or gene “knock-ins”. However, it has been difficult to identify cells that have edited receptors in unmanipulated mice and humans. To try to identify such cells we isolated and characterized B cells that coexpress surrogate and conventional light chains (V-preB+L+) from the blood of normal human donors. V-preB+L+ B cells express RAG mRNA, display an unusual heavy and light chain antibody repertoire consistent with antiself reactivity, and show evidence of receptor editing. These cells accumulate in the joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, consistent with a role for V-preB+L+ B cells and receptor editing in autoimmune disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goodnow, C. C. Balancing immunity and tolerance: deleting and tuning lymphocyte repertoires . Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 2264– 71 (1996).
Nemazee, D. Does immunological tolerance explain the waste in the B-lymphocyte immune system? Experiment and theory. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 764 , 397–401 (1995).
Radic, M. Z. & Weigert, M. Origins of anti-DNA antibodies and their implications for B-cell tolerance. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 764, 384–96 (1995).
Hertz, M. & Nemazee, D. BCR ligation induces receptor editing in IgM+IgD− bone marrow B cells in vitro. Immunity 6, 429– 436 (1997).
Melamed, D., Benschop, R. J., Cambier, J. C. & Nemazee, D. Developmental regulation of B lymphocyte immune tolerance compartmentalizes clonal selection from receptor selection. Cell 92, 173–82 (1998).
Gay, D., Saunders, T., Camper, S. & Weigert, M. Receptor editing: an approach by autoreactive B cells to escape tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 177, 999–1008 ( 1993).
Radic, M.Z., Erickson, J., Litwin, S. & Weigert, M. B lymphocytes may escape tolerance by revising their antigen receptors. J. Exp. Med. 177, 1165–1173 ( 1993).
Tiegs, S. L., Russell, D. M. & Nemazee, D. Receptor editing in self-reactive bone marrow B cells . J. Exp. Med. 177, 1009– 1020 (1993).
Chen, C., Prak, E. L. & Weigert, M. Editing disease-associated autoantibodies. Immunity 6, 97–105 ( 1997).
Pelanda, R. et al. Receptor editing in a transgenic mouse model: site, efficiency, and role in B cell tolerance and antibody diversification. Immunity 7, 765–75 ( 1997).
Xu, H., Li, H., Suri-Payer, E., Hardy, R. R. & Weigert, M. Regulation of anti-DNA B cells in recombination-activating gene-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 188, 1247 –54 (1998).
Reth, M., Gehrmann, P., Petrac, E. & Wiese, P. A novel VH to VH(D)JH joining mechanism in heavy-chain-negative (null) pre-B cells results in heavy-chain production. Nature 322, 840–2 (1986).
Chen, C., Nagy, Z., Prak, E. L. & Weigert, M. Immunoglobulin heavy chain gene replacement: a mechanism of receptor editing. Immunity 3, 747–55 ( 1995).
Taki, S., Schwenk, F. & Rajewsky, K. Rearrangement of upstream DH and VH genes to a rearranged immunoglobulin variable region gene inserted into the DQ52-JH region of the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus . Eur. J. Immunol. 25, 1888– 96 (1995).
Prak, E. L. & Weigert, M. Light chain replacement: a new model for antibody gene rearrangement. J. Exp. Med. 182, 541–8 (1995).
Retter, M. W. & Nemazee, D. Receptor editing occurs frequently during normal B cell development. J. Exp. Med. 188, 1231–8 (1998).
Wilson, P. C. et al. Receptor revision of immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region genes in normal human B lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 191 ,1881–94 (2000).
Klein, U., Rajewsky, K. & Kuppers, R. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of human peripheral blood B-cell subsets with special reference to N-region addition and J κ-usage in Vκ Jκ-joints and κ/λ ratios in naive versus memory B-cell subsets to identify traces of receptor editing processes. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 246 , 141–6 (1999).
Giachino, C., Padovan, E. & Lanzavecchia, A. Re-expression of RAG-1 and RAG-2 genes and evidence for secondary rearrangements in human germinal center B lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 28, 3506–13 (1998).
de Wildt, R. M., Hoet, R. M. A., van Venrooij, W. J., Tomlinson, I. M. & Winter, G. Analysis of heavy and light chain pairings indicates that receptor editing shapes the human antibody repertoire. J. Mol. Biol. 285, 895–901 (1999).
Brard, F., Shannon, M., Prak, E. L., Litwin, S. & Weigert, M. Somatic mutation and light chain rearrangement generate autoimmunity in anti-single-stranded DNA transgenic MRL/lpr mice. J. Exp. Med. 190, 691–704 (1999).
Dorner, T., Foster, S.J., Farner, N.L. & Lipsky, P.E. Immunoglobulin κ chain receptor editing in systemic lupus erythematosus . J. Clin. Invest. 102, 688– 94 (1998).
Dorner, T., Farner, N. L. & Lipsky, P. E. Ig λ and heavy chain gene usage in early untreated systemic lupus erythematosus suggests intensive B cell stimulation. J. Immunol. 163, 1027–36 (1999).
Meffre, E. et al. Antigen receptor engagement turns off the V(D)J recombination machinery in human tonsil B cells. J. Exp. Med. 188 , 765–72 (1998).
Wang, Y. H., Nomura, J., Faye-Petersen, O. M. & Cooper, M. D. Surrogate light chain production during B cell differentiation: differential intracellular versus cell surface expression. J. Immunol. 161, 1132–9 (1998).
Lemmers, B., Gauthier, L., Guelpa-Fonlupt, V., Fougereau, M. & Schiff, C. The human (PsiL+mu−) proB complex: cell surface expression and biochemical structure of a putative transducing receptor. Blood 93, 4336–46 (1999).
Uckun, F. M. Regulation of human B-cell ontogeny. Blood 76, 1908–23 (1990).
Pascual, V. et al. Analysis of somatic mutation in five B cell subsets of human tonsil. J. Exp. Med. 180, 329– 339 (1994).
Liu, Y. J. et al. Normal human IgD+IgM− germinal center B cells can express up to 80 mutations in the variable region of their IgD transcripts. Immunity 4, 603 –13 (1996).
Klein, U., Rajewsky, K. & Kuppers, R. Human immunoglobulin (Ig)M+IgD+ peripheral blood B cells expressing the CD27 cell surface antigen carry somatically mutated variable region genes: CD27 as a general marker for somatically mutated (memory) B cells. J. Exp. Med. 188, 1679–89 (1998).
Yu, W. et al. Continued RAG expression in late stages of B cell development and no apparent re–induction after immunization. Nature 400, 682–7 (1999).
Monroe, R. et al. RAG2:GFP knockin mice reveal novel aspects of RAG2 expression in primary and peripheral lymphoid tissues. Immunity 11, 201–212 (1999).
Tangye, S. G., Liu, Y. J., Aversa, G., Phillips, J. H. & de Vries, J. E. Identification of functional human splenic memory B cells by expression of CD148 and CD27. J. Exp. Med. 188, 1691–703 (1998).
Conley, M. E. B cells in patients with X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J. Immunol. 134, 3070–4 ( 1985).
Lassoued, K. et al. Expression of surrogate light chain receptors is restricted to a late stage in pre-B cell differentiation. Cell 73, 73–86 (1993).
Guelpa-Fonlupt, V., Tonnelle, C., Blaise, D., Fougereau, M. & Fumoux, F. Discrete early pro-B and pre-B stages in normal human bone marrow as defined by surface pseudo-light chain expression. Eur. J. Immunol. 24, 257–64 (1994).
Ghia, P. et al. Ordering of human bone marrow B lymphocyte precursors by single-cell polymerase chain reaction analyses of the rearrangement status of the immunoglobulin H and L chain loci. J. Exp. Med. 184, 2217 –2229 (1996).
Sanz, I. et al. The smaller human VH gene families display remarkably little polymorphism. EMBO J. 8, 3741– 8 (1989).
Yamada, M. et al. Preferential utilization of specific immunoglobulin heavy chain diversity and joining segments in adult human peripheral blood B lymphocytes . J. Exp. Med. 173, 395– 407 (1991).
Brezinschek, H. P. et al. Analysis of the human VH gene repertoire. Differential effects of selection and somatic hypermutation on human peripheral CD5(+)/IgM+ and CD5(−)/IgM+ B cells. J. Clin. Invest. 99, 2488–501 (1997).
Corbett, S. J., Tomlinson, I. M., Sonnhammer, E. L. L., Buck, D. & Winter, G. Sequence of the human immunoglobulin diversity (D) segment locus: a systematic analysis provides no evidence for the use of DIR segments, inverted D segments, “minor” D segments or D-D recombination. J. Mol. Biol. 270, 587–97 (1997).
Meek, K. D., Hasemann, C. A. & Capra, J. D. Novel rearrangements at the immunoglobulin D locus. Inversions and fusions add to IgH somatic diversity. J. Exp. Med. 170, 39–57 ( 1989).
Klonowski, K. D., Primiano, L. L. & Monestier, M. Atypical VH-D-JH rearrangements in newborn autoimmune MRL mice. J. Immunol. 162, 1566–72 (1999).
Ichiyoshi, Y. & Casali, P. Analysis of the structural correlates for antibody polyreactivity by multiple reassortments of chimeric human immunoglobulin heavy and light chain V segments. J. Exp. Med. 180, 885–95 (1994).
Crouzier, R., Martin, T. & Pasquali, J. L. Heavy chain variable region, light chain variable region, and heavy chain CDR3 influences on the mono- and polyreactivity and on the affinity of human monoclonal rheumatoid factors. J. Immunol. 154, 4526–35 ( 1995).
Han, S., Zheng, B., Schatz, D. G., Spanopoulou, E. & Kelsoe, G. Neoteny in lymphocytes: Rag1 and Rag2 expression in germinal center B cells. Science 274, 2094 –7 (1996).
Hikida, M. et al. Reexpression of RAG-1 and RAG-2 Genes in Activated Mature Mouse B cells. Science 274, 2092– 2094 (1996).
Han, S. et al. V(D)J recombinase activity in a subset of germinal center B lymphocytes . Science 278, 301–305 (1997).
Hikida, M., Mori, M., Kawabata, T., Takai, T. & Ohmori, H. Characterization of B cells expressing Recombination Activating Genes in germinal centers of immunized mouse lymph nodes. J. Immunol. 158, 2509–2512 ( 1997).
Papavasiliou, F. et al. V(D)J Recombination in Mature B cells a New Mechanism for Diversification of Antibody Responses. Science 278, 298–301 (1997).
Hertz, M., Kouskoff, V., Nakamura, T. & Nemazee, D. V(D)J recombinase induction in splenic B lymphocytes is inhibited by antigen-receptor signaling. Nature 394, 292– 5 (1998).
Foster, S. J., Brezinschek, H. P., Brezinschek, R. I. & Lipsky, P. E. Molecular mechanisms and selective influences that shape the κ gene repertoire of IgM+ B cells. J. Clin. Invest. 99, 1614–27 (1997).
Schable, K. F. & Zachau, H. G. The variable genes of the human immunoglobulin kappa locus. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 374, 1001–22 ( 1993).
Victor, K. D. et al. Rheumatoid factors isolated from patients with autoimmune disorders are derived from germline genes distinct from those encoding the Wa, Po, and Bla cross-reactive idiotypes. J. Clin. Invest. 87, 1603–13 (1991).
Bridges, S.L. Jr et al. Somatic mutation and CDR3 lengths of immunoglobulin kappa light chains expressed in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and in normal individuals. J. Clin. Invest. 96, 831–41 (1995).
Randen, I., Mellbye, O. J., Forre, O. & Natvig, J. B. The identification of germinal centres and follicular dendritic cell networks in rheumatoid synovial tissue. Scand J. Immunol. 41 , 481–6 (1995).
Gauthier, L., Lemmers, B., Guelpa-Fonlupt, V., Fougereau, M. & Schiff, C. Mu-surrogate light chain physicochemical interactions of the human preB cell receptor: implications for VH repertoire selection and cell signaling at the preB cell stage. J. Immunol. 162, 41–50 ( 1999).
Mian, I. S., Bradwell, A. R. & Olson, A. J. Structure, function and properties of antibody binding sites. J. Mol. Biol. 217, 133– 51 (1991).
Manheimer-Lory, A. J., Zandman-Goddard, G., Davidson, A., Aranow, C. & Diamond, B. Lupus-specific antibodies reveal an altered pattern of somatic mutation. J. Clin. Invest. 100, 2538–46 (1997).
Erikson, J. et al. Expression of anti-DNA immunoglobulin transgenes in non-autoimmune mice. Nature 349, 331–4 (1991).
Goodnow, C. C., Crosbie, J., Jorgensen, H., Brink, R. A. & Basten, A. Induction of self-tolerance in mature peripheral B lymphocytes. Nature 342, 385 –391 (1989).
Paramithiotis, E. & Cooper, M. D. Memory B lymphocytes migrate to bone marrow in humans. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 208–12 (1997).
Meffre, E. et al. A human non-XLA immunodeficiency disease characterized by blockage of B cell development at an early proB cell stage. J. Clin. Invest. 98, 1519–26 (1996).
Acknowledgements
We thank the Nussenzweig lab for comments and discussions; G. Michel, H. Chambost and C. Fossat for blood samples; W. Muller and K. Tai for tonsil and joint samples and P. Wilson, J. D. Capra and N. Chiorazzi for sharing unpublished data. Supported by grants from the NIH (to M.C.N. and J.W.Y.) and the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (to J.W.Y.). M.C.N. is based at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meffre, E., Davis, E., Schiff, C. et al. Circulating human B cells that express surrogate light chains and edited receptors. Nat Immunol 1, 207–213 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/79739
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/79739
This article is cited by
-
Peripheral VH4+ plasmablasts demonstrate autoreactive B cell expansion toward brain antigens in early multiple sclerosis patients
Acta Neuropathologica (2017)
-
IGHV gene features and MYD88 L265P mutation separate the three marginal zone lymphoma entities and Waldenström macroglobulinemia/lymphoplasmacytic lymphomas
Leukemia (2013)
-
B cells in HIV infection and disease
Nature Reviews Immunology (2009)
-
Giving B cell tolerance the 'TSLiP'
Nature Immunology (2007)
-
Indications for peripheral light-chain revision and somatic hypermutation without a functional B-cell receptor in precursors of a composite diffuse large B-cell and Hodgkin's lymphoma
Laboratory Investigation (2004)