Abstract
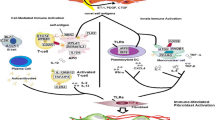
The importance of the genetic component in the pathogenesis of scleroderma, or systemic sclerosis, has been strengthened in the past 2 years with studies on genetic markers–either candidate gene or genome-wide association studies—in large case–control series. Multiple genes have been consistently associated with susceptibility to scleroderma, and interestingly, several of them are involved in immune regulation. Because many of these genes are shared with other autoimmune diseases, a common underlying autoimmune mechanism has been proposed. The challenge that lies ahead is to confirm these associations and to find markers or pathways that are unique to scleroderma and that may define its distinctive phenotype.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Abraham DJ, Krieg T, Distler J, et al.: Overview of pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009, 48(Suppl 3):iii3–iii7.
• Frech T, Khanna D, Markewitz B, et al.: Heritability of vasculopathy, autoimmune disease, and fibrosis in systemic sclerosis: a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum 2010, 62:2109–2116. This article analyzed the heritability of some of the clinical manifestations of SSc.
Mayes MD, Lacey JV Jr, Beebe-Dimmer J, et al.: Prevalence, incidence, survival, and disease characteristics of systemic sclerosis in a large US population. Arthritis Rheum 2003, 48:2246–2255.
Allanore Y, Dieude P, Boileau C: Genetic background of systemic sclerosis: autoimmune genes take centre stage. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2010, 49:203–210.
•• Radstake TR, Gorlova O, Rueda B, et al.: Genome-wide association study of systemic sclerosis identifies CD247 as a new susceptibility locus. Nat Genet 2010, 42:426–429. This large, multicenter GWAS in SSc identified a novel area of susceptibility and confirmed an association with areas related to immune response.
• Zhou X, Lee JE, Arnett FC, et al.: HLA-DPB1 and DPB2 are genetic loci for systemic sclerosis: a genome-wide association study in Koreans with replication in North Americans. Arthritis Rheum 2009, 60:3807–3814. This was a GWAS in a small homogeneous population, with a strong association with an HLA region.
Agarwal SK, Tan FK, Arnett FC: Genetics and genomic studies in scleroderma (systemic sclerosis). Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2008, 34:17–40.
• Arnett FC, Gourh P, Shete S, et al.: Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II alleles, haplotypes and epitopes which confer susceptibility or protection in systemic sclerosis: analyses in 1300 Caucasian, African-American and Hispanic cases and 1000 controls. Ann Rheum Dis 2010, 69:822–827. This was a comprehensive analysis of the HLA region in a large cohort of SSc patients with comparison between different ethnic backgrounds.
Simeon CP, Fonollosa V, Tolosa C, et al.: Association of HLA class II genes with systemic sclerosis in Spanish patients. J Rheumatol 2009, 36:2733–2736.
Assassi S, Del JD, Sutter K, et al.: Clinical and genetic factors predictive of mortality in early systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 2009, 61:1403–1411.
Karp DR, Marthandan N, Marsh SG, et al.: Novel sequence feature variant type analysis of the HLA genetic association in systemic sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet 2010, 19:707–719.
Milano A, Pendergrass SA, Sargent JL, et al.: Molecular subsets in the gene expression signatures of scleroderma skin. PLoS One 2008, 3:e2696.
Assassi S, Mayes MD, Arnett FC, et al.: Systemic sclerosis and lupus: points in an interferon-mediated continuum. Arthritis Rheum 2010, 62:589–598.
• Dieude P, Guedj M, Wipff J, et al.: STAT4 is a genetic risk factor for systemic sclerosis having additive effects with IRF5 on disease susceptibility and related pulmonary fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum 2009, 60:2472–2479. This study identified IRF5 and STAT4—genes previously associated with other autoimmune disease—their association with SSc, and the presence of additive effects between these markers.
Dieude P, Dawidowicz K, Guedj M, et al.: Phenotype-haplotype correlation of IRF5 in systemic sclerosis: role of 2 haplotypes in disease severity. J Rheumatol 2010, 37:987–992.
Ito I, Kawaguchi Y, Kawasaki A, et al.: Association of a functional polymorphism in the IRF5 region with systemic sclerosis in a Japanese population. Arthritis Rheum 2009, 60:1845–1850.
Rueda B, Broen J, Simeon C, et al.: The STAT4 gene influences the genetic predisposition to systemic sclerosis phenotype. Hum Mol Genet 2009, 18:2071–2077.
Tsuchiya N, Kawasaki A, Hasegawa M, et al.: Association of STAT4 polymorphism with systemic sclerosis in a Japanese population. Ann Rheum Dis 2009, 68:1375–1376.
Gourh P, Agarwal SK, Divecha D, et al.: Polymorphisms in TBX21 and STAT4 increase the risk of systemic sclerosis: evidence of possible gene-gene interaction and alterations in Th1/Th2 cytokines. Arthritis Rheum 2009, 60:3794–3806.
• Dieude P, Wipff J, Guedj M, et al.: BANK1 is a genetic risk factor for diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis and has additive effects with IRF5 and STAT4. Arthritis Rheum 2009, 60:3447–3454. This study showed the association of SSc with another gene implicated in immune regulation and provided evidence of the interaction between IRF5 and STAT4 SNPs in the SSc susceptibility.
Rueda B, Gourh P, Broen J, et al.: BANK1 functional variants are associated with susceptibility to diffuse systemic sclerosis in Caucasians. Ann Rheum Dis 2010, 69:700–705.
Hom G, Graham RR, Modrek B, et al.: Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13-BLK and ITGAM-ITGAX. N Engl J Med 2008, 358:900–909.
Gourh P, Agarwal SK, Martin E, et al.: Association of the C8orf13-BLK region with systemic sclerosis in North-American and European populations. J Autoimmun 2010, 34:155–162.
Ito I, Kawaguchi Y, Kawasaki A, et al.: Association of the FAM167A-BLK region with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 2010, 62:890–895.
Delgado-Vega AM, Abelson AK, Sanchez E, et al.: Replication of the TNFSF4 (OX40L) promoter region association with systemic lupus erythematosus. Genes Immun 2009, 10:248–253.
Gourh P, Arnett FC, Tan FK, et al.: Association of TNFSF4 (OX40L) polymorphisms with susceptibility to systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 2010, 69:550–555.
Musone SL, Taylor KE, Lu TT, et al.: Multiple polymorphisms in the TNFAIP3 region are independently associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 2008, 40:1062–1064.
Graham RR, Cotsapas C, Davies L, et al.: Genetic variants near TNFAIP3 on 6q23 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 2008, 40:1059–1061.
Liakouli V, Manetti M, Pacini A, et al.: The -670 G > A polymorphism in the FAS gene promoter region influences the susceptibility to systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 2009, 68:584–590.
Broen J, Gourh P, Rueda B, et al.: The FAS -670A > G polymorphism influences susceptibility to systemic sclerosis phenotypes. Arthritis Rheum 2009, 60:3815–3820.
Park WS, Firth AL, Han J, et al.: Patho-, physiological roles of voltage-dependent K + channels in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. J Smooth Muscle Res 2010, 46:89–105.
Wipff J, Dieude P, Guedj M, et al.: Association of KCNA5 gene polymorphism with systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension in the European Caucasian population. Arthritis Rheum 2010 Jun 15 (Epub ahead of print).
Leask A, Abraham DJ: All in the CCN family: essential matricellular signaling modulators emerge from the bunker. J Cell Sci 2006, 119:4803–4810.
Leask A, Parapuram SK, Shi-wen X, et al.: Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF, CCN2) gene regulation: a potent clinical bio-marker of fibroproliferative disease? J Cell Commun Signal 2009, 3:89–94.
Fonseca C, Lindahl GE, Ponticos M, et al.: A polymorphism in the CTGF promoter region associated with systemic sclerosis. N Engl J Med 2007, 357:1210–1220.
Kawaguchi Y, Ota Y, Kawamoto M, et al.: Association study of a polymorphism of the CTGF gene and susceptibility to systemic sclerosis in the Japanese population. Ann Rheum Dis 2009, 68:1921–1924.
Gourh P, Mayes MD, Arnett FC: CTGF polymorphism associated with systemic sclerosis. N Engl J Med 2008, 358:308–309.
Rueda B, Simeon C, Hesselstrand R, et al.: A large multicentre analysis of CTGF -945 promoter polymorphism does not confirm association with systemic sclerosis susceptibility or phenotype. Ann Rheum Dis 2009, 68:1618–1620.
Granel B, Argiro L, Hachulla E, et al.: Association between a CTGF gene polymorphism and systemic sclerosis in a French population. J Rheumatol 2010, 37:351–358.
Alizadeh BZ, Broen J, Rueda B, et al.: Functional variants of Fc gamma receptor (FCGR2A) and FCGR3A are not associated with susceptibility to systemic sclerosis in a large European Study (EUSTAR). J Rheumatol 2010, 37:1673–1679.
Wipff J, Gallier G, Dieude P, et al.: Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene does not contribute to genetic susceptibility to systemic sclerosis in European Caucasians. J Rheumatol 2009, 36:337–340.
Wipff J, Bonnet P, Ruiz B, et al.: Association study of serotonin transporter gene (SLC6A4) in systemic sclerosis in European Caucasian populations. J Rheumatol 2010, 37:1164–1167.
Carulli MT, Spagnolo P, Fonseca C, et al.: Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in CCL2 gene are not associated with susceptibility to systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 2008, 35:839–844.
Radstake TR, Vonk MC, Dekkers M, et al.: The -2518A > G promoter polymorphism in the CCL2 gene is not associated with systemic sclerosis susceptibility or phenotype: results from a multicenter study of European Caucasian patients. Hum Immunol 2009, 70:130–133.
Wipff J, Dieude P, Avouac J, et al.: Association of metalloproteinase gene polymorphisms with systemic sclerosis in the European Caucasian population. J Rheumatol 2010, 37:599–602.
Wipff J, Giraud M, Sibilia J, et al.: Polymorphic markers of the fibrillin-1 gene and systemic sclerosis in European Caucasian patients. J Rheumatol 2008, 35:643–649.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants SAF2009-11110, Junta de Andalucía; grants CTS-4977 and CTS-180; and by the RETICS Program, RD08/0075 (RIER) from Instituto de Salud Carlos III (to Dr. Martin) and by the Raynaud’s and Scleroderma Association, Arthritis Research UK, and the Scleroderma Society (Dr. Fonseca).
Disclosure
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, J., Fonseca, C. The Genetics of Scleroderma. Curr Rheumatol Rep 13, 13–20 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-010-0139-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-010-0139-5