Abstract
Objective
This study was to investigate the evidence for complement activation in renal biopsy specimens of patients with myeloperoxidase (MPO)-antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA)-associated pauci-immune vasculitis.
Methods
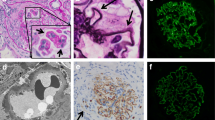
Renal biopsy specimens from seven patients with MPO-ANCA positive pauci-immune necrotizing crescentic glomerulonephritis (NCGN) were used to detect the staining of membrane attack complex (MAC), C3d, C4d, mannose-binding lectin (MBL), factor B and factor P using immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence. Renal tissue from seven patients with minimal change disease (MCD) and two normal renal tissue were used as controls.
Results
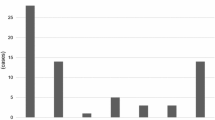
MAC, C3d, factor B and factor P could be detected in glomeruli and small blood vessels with active vasculitis of patients with pauci-immune AAV, but not or scarcely in patients with MCD and in normal renal tissue. C3d and factor B co-localized with MAC, factor P colocalized with C3d. MBL and C4d were not detected in patients with AAV.
Conclusion
The alternative pathway of the complement system is involved in renal damage of human pauci-immune AAV.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANCA:
-
antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody
- AAV:
-
ANCA-associated vasculitis
- MPO:
-
myeloperoxidase
- MBL:
-
mannose-binding lectin
- MAC:
-
membrane attack complex
- MCD:
-
minimal change disease
- NCGN:
-
necrotizing crescentic glomerulonephritis
References
Falk RJ, Jennette JC. ANCA small-vessel vasculitis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997;8:314–22. doi:10.1159/000106649.
Xiao H, Heeringa P, Hu P, Liu Z, Zhao M, Aratani Y, et al. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies specific for myeloperoxidase cause glomerulonephritis and vasculitis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2002;110:955–63.
Xiao H, Schreiber A, Heeringa P. Alternative complement pathway in the pathogenesis of disease mediated by antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies. Am J Pathol. 2007;170:52–64. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2007.060573.
Huugen D, Esch AV, Xiao H, Peutz-kootstra CJ, Buuman WA, Tervaert JW, et al. Inhibition of complement factor C5 protects against anti-myeloperoxidase antibody-mediated glomerulonephritis in mice. Kidney Int. 2007;71:646–54. doi:10.1038/sj.ki.5002103.
Welch TR, Beischel LS, Witte DP. Differential expression of complement C3 and C4 in the human kidney. J Clin Invest. 1993;92:1451–8. doi:10.1172/JCI116722.
Passwell J, Schreiner GF, Nonaka M, Beuscher HU, Colten HR. Local extrahepatic expression of complement genes C3, factor B, C2, and C4 is increased in murine lupus nephritis. J Clin Invest. 1988;82:1676–84. doi:10.1172/JCI113780.
Hinglais N, Kazatchkine MD, Bhakdi S, Appay MD, Mandet C, Grossetete J, et al. Immunohistochemical study of the C5b-9 complex of complement in human kidneys. Kidney Int. 1986;30:399–410. doi:10.1038/ki.1986.198.
Haas M, Eustace JA. Immune complex deposits in ANCA-associated crescentic glomerulonephritis: A study of 126 cases. Kidney Int. 2004;65:2145–52. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00632.x.
Neumann I, Regele H, Kain R, Birck R, Meis FT. Glomerular immune deposits are associated with increased proteinuria in patients with ANCA-associated crescentic nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003;18:524–31. doi:10.1093/ndt/18.3.524.
Yu F, Chen M, Gao Y, Wang SX, Zou WZ, Zhao MH, et al. Clinical and pathological features of renal involvement in propylthiouracil-associated ANCA-positive vasculitis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49:607–14. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.01.021.
Sacks SH, Zhou W: New Boundaries for Complement in Renal Disease, J Am Soc Nephrol Express. Published on February 6, 2008 as doi: 10.1681/ASN.2007101121. Epub ahead of print.
Van Wijngaarden RAFL, Hauer HA, Wolterbeek R, Jayne DRW, Gaskin G, Rasmussen N, for the European Vasculitis Study Group (EUVAS), et al. Clinical and histologic determinants of renal outcome in ANCA-associated vasculitis: A prospective analysis of 100 patients with severe renal involvement. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:2264–74. doi:10.1681/ASN.2005080870.
Hauer HA, Bajema IM, van Houwelingen HC, Ferrario F, Noël LH, Waldherr R, et al. European Vasculitis Study Group (EUVAS): Renal histology in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Differences between diagnostic and serologic subgroups. Kidney Int. 2002;61:80–9. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00089.x.
Chen M, Yu F, Zhang Y, Zhao MH. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated vasculitis in older patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2008;87:203–9.
Sahu A, Lambris JD. Structure and biology of complement protein C3, a connecting link between innate and acquired immunity. Immunol Rev. 2001;180:35–48. doi:10.1034/j.1600-065X.2001.1800103.x.
Schulze M, Pruchno CJ, Burns M, Baker PJ, Johnson RJ, Couser WG. Glomerular C3c localization indicates ongoing immune deposit formation and complement activation in experimental glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol. 1993;142:179–87.
Kilgore KS, Ward PA, Warren JS. Neutrophil adhesion to human endothelial cells is induced by the membrane attack complex: The roles of P-selectin and platelet activating factor. Inflammation 1998;22:583–98. doi:10.1023/A:1022362413939.
Xiao H, Heeringa P, Liu Z, Huugen D, Hu P, Maeda N, et al. The role of neutrophils in the induction of glomerulonephritis by anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies. Am J Pathol. 2005;167:39–45.
Chakravarti DN, Campbell RD, Porter RR. The chemical structure of the C4d fragment of the human complement component C4. Mol Immunol. 1987;24:1187–97. doi:10.1016/0161-5890(87)90165-9.
Colvin RB. Antibody-mediated renal allograft rejection: diagnosis and pathogenesis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:1046–56. doi:10.1681/ASN.2007010073.
Petersen SV, Thiel S, Jensenius JC. The mannose-binding lectin pathway of complement activation: Biology and disease association. Mol Immunol. 2001;38:133–49. doi:10.1016/S0161-5890(01)00038-4.
Hisano S, Matsushita M, Fujita T, Endo Y, Takebayashi S. Mesangial IgA2 deposits and lectin pathway-mediated complement activation in IgA glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;38:1082–8. doi:10.1053/ajkd.2001.28611.
Roos A, Rastaldi MP, Calvaresi N. Glomerular activation of the lectin pathway of complement in IgA nephropathy Is associated with more severe renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:1724–34. doi:10.1681/ASN.2005090923.
Ruth AJ, Kitching AR, Kwan RY, Odobasic D, Ooi JD, Timoshanko JR, et al. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and effector CD4+ cells play nonredundant roles in anti-myeloperoxidase crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:1940–9. doi:10.1681/ASN.2006020108.
Schwaeble WJ, Reid KB. Does properdin crosslink the cellular and the humoral immune response? Immunol Today. 1999;20:17–21. doi:10.1016/S0167-5699(98)01376-0.
Moll S, Miot S, Sadallah S, Gudat F, Mihatsch MJ, Schifferli JA. No complement receptor 1 stumps on podocytes in human glomerulopathies. Kidney Int. 2001;59:160–8. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.00476.x.
Nomura A, Nishikawa K, Yuzawa Y, Okada H, Okada N, Morgan BP. Tubulointerstitial injury induced in rats by a monoclonal antibody that inhibits function of a membrane inhibitor of complement. J Clin Invest. 1995;96:348–56. doi:10.1172/JCI118291.
Nangaku M. Complement regulatory proteins in glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. 1998;54:1419–28. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.1998.00130.x.
Jennette JC, Thomas DB. Pauci-immune and antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody associated crescentic glomerulonephritis and vasculitis. In: Jennette JC, Olson JL, Schwartz MM, Silva FG, editors. Hepinstall’s pathology of the kidney. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. p. 652.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by a grant from National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No.30725034) and a grant of the Chinese 985 project (985-2-104-113). P. Heeringa is supported by a grant from the Dutch Organization for Scientific research (NWO VIDI 917.66.342) and by a grant from the Dutch Kidney Foundation (PC 07-2204).
We are very grateful to Dr. Wan-zhong Zou and Dr. Chen Wang for assistance in the scoring and collecting pathological data of the patients.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, Gq., Chen, M., Liu, G. et al. Complement Activation Is Involved in Renal Damage in Human Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody Associated Pauci-Immune Vasculitis. J Clin Immunol 29, 282–291 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-008-9268-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-008-9268-2