Abstract
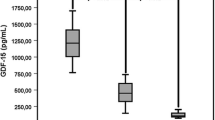
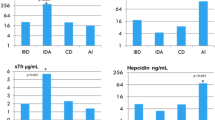
Hepcidin is a key hormone governing mammalian iron homeostasis and may be directly or indirectly involved in the development of most iron deficiency/overload and inflammation-induced anemia. The objective of this study was to investigate the expression of hepcidin in anemia of chronic disease. To characterize serum hepcidin, iron and inflammatory indicators associated with anemia of chronic disease (ACD), we studied ACD, ACD concomitant iron-deficiency anemia (ACD/IDA), pure IDA and acute inflammation (AcI) patients and analyzed the associations between hepcidin levels and inflammation parameters in various types of anemia. Serum hepcidin levels in patient groups were statistically different, from high to low: ACD, AcI > ACD/IDA > the control > IDA. Serum ferritin levels were significantly increased in ACD and AcI patients but were decreased significantly in ACD/IDA and IDA. Elevated serum EPO concentrations were found in ACD, ACD/IDA and IDA patients but not in AcI patients and the controls. A positive correlation between hepcidin and IL-6 levels only existed in ACD/IDA, AcI and the control groups. A positive correlation between hepcidin and ferritin was marked in the control group, while a negative correlation between hepcidin and ferritin was noted in IDA. The significant negative correlation between hepcidin expression and reticulocyte count was marked in both ACD/IDA and IDA groups. All of these data demonstrated that hepcidin might play role in pathogenesis of ACD, ACD/IDA and IDA, and it could be a potential marker for detection and differentiation of these anemias.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weiss G (2002) Pathogenesis and treatment of anaemia of chronic disease. Blood Rev 16:87–96
Weiss G, Goodnough LT (2005) Anemia of chronic disease. N Engl J Med 352:1011–1023
Jurado RL (1997) Iron, infections, and anemia of inflammation. Clin Infect Dis 25:888–895
Brugnara C (2003) Iron deficiency and erythropoiesis: new diagnostic approaches. Clin Chem 49:1573–1578
Thomas C, Thomas L (2002) Biochemical markers and hematologic indices in the diagnosis of functional iron deficiency. Clin Chem 48:1066–1076
Metzgeroth G, Adelberger V, Dorn-Beineke A, Kuhn C, Schatz M, Maywald O, Bertsch T, Wisser H, Hehlmann R, Hastka J (2005) Soluble transferrin receptor and zinc protoporphyrin—competitors or efficient partners? Eur J Haematol 75:309–317
Weinstein DA, Roy CN, Fleming MD, Loda MF, Wolfsdorf JI, Andrews NC (2002) Inappropriate expression of hepcidin is associated with iron refractory anemia: implications for the anemia of chronic disease. Blood 100:3776–3781
Nemeth E, Rivera S, Gabayan V, Keller C, Taudorf S, Pedersen BK, Ganz T (2004) Il-6 mediates hypoferremia of inflammation by inducing the synthesis of the iron regulatory hormone hepcidin. J Clin Invest 113:1271–1276
Nemeth E, Ganz T (2006) Hepcidin and iron-loading anemias. Haematologica 91:727–732
Nemeth E, Tuttle MS, Powelson J, Vaughn MB, Donovan A, Ward DM, Ganz T, Kaplan J (2004) Hepcidin regulates cellular iron efflux by binding to ferroportin and inducing its internalization. Science 306:2090–2093
Kemna EH, Tjalsma H, Willems HL, Swinkels DW (2008) Hepcidin: from discovery to differential diagnosis. Haematologica 93:90–97
Kemna EH, Tjalsma H, Podust VN, Swinkels DW (2007) Mass spectrometry-based hepcidin measurements in serum and urine: analytical aspects and clinical implications. Clin Chem 53:620–628
Nemeth E, Valore EV, Territo M, Schiller G, Lichtenstein A, Ganz T (2003) Hepcidin, a putative mediator of anemia of inflammation, is a type ii acute-phase protein. Blood 101:2461–2463
Piperno A, Mariani R, Trombini P, Girelli D (2009) Hepcidin modulation in human diseases: from research to clinic. World J Gastroenterol 15:538–551
Theurl I, Aigner E, Theurl M, Nairz M, Seifert M, Schroll A, Sonnweber T, Eberwein L, Witcher DR, Murphy AT, Wroblewski VJ, Wurz E, Datz C, Weiss G (2009) Regulation of iron homeostasis in anemia of chronic disease and iron deficiency anemia: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Blood 113:5277–5286
Barosi G (1994) Inadequate erythropoietin response to anemia: definition and clinical relevance. Ann Hematol 68:215–223
Ganz T (2003) Hepcidin, a key regulator of iron metabolism and mediator of anemia of inflammation. Blood 102:783–788
Nicolas G, Bennoun M, Porteu A, Mativet S, Beaumont C, Grandchamp B, Sirito M, Sawadogo M, Kahn A, Vaulont S (2002) Severe iron deficiency anemia in transgenic mice expressing liver hepcidin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:4596–4601
Beutler E (2007) Iron storage disease: facts, fiction and progress. Blood Cells Mol Dis 39:140–147
Lee GR (1983) The anemia of chronic disease. Semin Hematol 20:61–80
Dallalio G, Law E, Means RT Jr (2006) Hepcidin inhibits in vitro erythroid colony formation at reduced erythropoietin concentrations. Blood 107:2702–2704
Fleming RE (2008) Iron and inflammation: cross-talk between pathways regulating hepcidin. J Mol Med 86:491–494
Ganz T (2006) Molecular pathogenesis of anemia of chronic disease. Pediatr Blood Cancer 46:554–557
De Domenico I, Ward DM, Kaplan J (2007) Hepcidin regulation: ironing out the details. J Clin Invest 117:1755–1758
Kemna E, Pickkers P, Nemeth E, van der Hoeven H, Swinkels D (2005) Time-course analysis of hepcidin, serum iron, and plasma cytokine levels in humans injected with lps. Blood 106:1864–1866
Theurl I, Mattle V, Seifert M, Mariani M, Marth C, Weiss G (2006) Dysregulated monocyte iron homeostasis and erythropoietin formation in patients with anemia of chronic disease. Blood 107:4142–4148
Ashby DR, Gale DP, Busbridge M, Murphy KG, Duncan ND, Cairns TD, Taube DH, Bloom SR, Tam FW, Chapman RS, Maxwell PH, Choi P (2009) Plasma hepcidin levels are elevated but responsive to erythropoietin therapy in renal disease. Kidney Int 75:976–981
Nicolas G, Chauvet C, Viatte L, Danan JL, Bigard X, Devaux I, Beaumont C, Kahn A, Vaulont S (2002) The gene encoding the iron regulatory peptide hepcidin is regulated by anemia, hypoxia, and inflammation. J Clin Invest 110:1037–1044
Pak M, Lopez MA, Gabayan V, Ganz T, Rivera S (2006) Suppression of hepcidin during anemia requires erythropoietic activity. Blood 108:3730–3735
Origa R, Galanello R, Ganz T, Giagu N, Maccioni L, Faa G, Nemeth E (2007) Liver iron concentrations and urinary hepcidin in beta-thalassemia. Haematologica 92:583–588
Kattamis A, Papassotiriou I, Palaiologou D, Apostolakou F, Galani A, Ladis V, Sakellaropoulos N, Papanikolaou G (2006) The effects of erythropoietic activity and iron burden on hepcidin expression in patients with thalassemia major. Haematologica 91:809–812
Vokurka M, Krijt J, Sulc K, Necas E (2006) Hepcidin mRNA levels in mouse liver respond to inhibition of erythropoiesis. Physiol Res 55:667–674
Kanda J, Mizumoto C, Kawabata H, Tsuchida H, Tomosugi N, Matsuo K, Uchiyama T (2008) Serum hepcidin level and erythropoietic activity after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 93:1550–1554
Nemeth E (2008) Iron regulation and erythropoiesis. Curr Opin Hematol 15:169–175
Pinto JP, Ribeiro S, Pontes H, Thowfeequ S, Tosh D, Carvalho F, Porto G (2008) Erythropoietin mediates hepcidin expression in hepatocytes through epor signaling and regulation of c/ebpalpha. Blood 111:5727–5733
Acknowledgments
This study were funded by Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (NO 9151008901000043) and Science and Technology Board of Shantou City, China [NO (2008)085]. The assistance of central laboratory of Shantou University Medical College was gratefully acknowledged. We are much obliged to the staff and students working in Medical Examination Center of the first affiliated Hospital of Shantou University Medical College for their help in our study.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Pp., Jiao, Xy., Wang, Xh. et al. Hepcidin expression in anemia of chronic disease and concomitant iron-deficiency anemia. Clin Exp Med 11, 33–42 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-010-0102-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-010-0102-9