Abstract
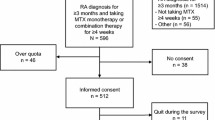
In rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, weekly intake of methotrexate (MTX) is the basic drug treatment. This observational study aims to investigate how many RA patients are adherent in terms of MTX intake and to identify determinants of non-adherence. Intake of MTX (orally or via injection) was recorded in 129 RA patients with an electronic monitoring system (MEMS®) during 16 weeks. In addition, two adherence questionnaires, the Medication Adherence Report Scale (MARS-5) and the Compliance-Questionnaire-Rheumatology (CQR) as well as a visual analogue scale (VAS) measuring MTX adherence, were administered to these patients. As possible determinants of adherence, data on demographics, disease and treatment characteristics, depression, illness cognitions, motivation, and social support were collected. Of all participants, 58 % were fully adherent and 75 % skipped at most one dose during 16 weeks. A better mental health status and suffering from comorbidities had a positive effect on adherence, while living alone had a negative effect. These three predictors explained 30 % of the variance in MTX adherence. Of the three self-report medication adherence measures, the VAS correlated the highest with the results of the electronic monitoring system (r = 0.552, p = 0.01). A relatively high adherence rate was observed in RA patients treated with MTX. The determinants identified by this study could be used to screen patients at risk for non-adherence. A simple VAS scale seems to be an acceptable way for a preliminary screening of MTX adherence.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prevoo ML, van’t Hof MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL (1995) Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38(1):44–48
Sutton S, Kinmonth A-L, Hardeman W, Hughes D, Boase S, Prevost AT et al (2014) Does electronic monitoring influence adherence to medication? randomized controlled trial of measurement reactivity. Ann Behav Med Publ Soc Behav Med 48(3):293–299
Waimann CA, Marengo MF, de Achaval S, Cox VL, Garcia-Gonzalez A, Reveille JD et al (2013) Electronic monitoring of oral therapies in ethnically diverse and economically disadvantaged patients with rheumatoid arthritis: consequences of low adherence. Arthritis Rheum 65(6):1421–1429
de Klerk E, van der Heijde D, Landewé R, van der Tempel H, Urquhart J, van der Linden S (2003) Patient compliance in rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, and gout. J Rheumatol 30(1):44–54
de Klerk E, van der Heijde D, van der Tempel H, van der Linden S (1999) Development of a questionnaire to investigate patient compliance with antirheumatic drug therapy. J Rheumatol 26(12):2635–2641
de Klerk E, van der Heijde D, Landewé R, van der Tempel H, van der Linden S (2003) The compliance-questionnaire-rheumatology compared with electronic medication event monitoring: a validation study. J Rheumatol 30(11):2469–2475
Salt E, Hall L, Peden AR, Home R (2012) Psychometric properties of three medication adherence scales in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Nurs Meas 20(1):59–72
Pasma A, van’t Spijker A, Hazes JMW, Busschbach JJV, Luime JJ (2013) Factors associated with adherence to pharmaceutical treatment for rheumatoid arthritis patients: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 43(1):18–28
López-González R, León L, Loza E, Redondo M, de Yébenes MJ G, Carmona L (2015) Adherence to biologic therapies and associated factors in rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis: a systematic literature review. Clin Exp Rheumatol 33(4):559–569
Pascual-Ramos V, Contreras-Yáñez I (2013) Motivations for inadequate persistence with disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in early rheumatoid arthritis: the patient’s perspective. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 14:336
Cabrera-Marroquín R, Contreras-Yáñez I, Alcocer-Castillejos N, Pascual-Ramos V (2014) Major depressive episodes are associated with poor concordance with therapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients: the impact on disease outcomes. Clin Exp Rheumatol 32(6):904–913
Bruce B, Fries JF (2003) The Stanford health assessment questionnaire: dimensions and practical applications. Health Qual Life Outcomes 1:20
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JBW (2002) The PHQ-15: validity of a new measure for evaluating the severity of somatic symptoms. Psychosom Med 64(2):258–266
Aaronson NK, Muller M, Cohen PD, Essink-Bot ML, Fekkes M, Sanderman R et al (1998) Translation, validation, and norming of the Dutch language version of the SF-36 health survey in community and chronic disease populations. J Clin Epidemiol 51(11):1055–1068
Martin A, Rief W, Klaiberg A, Braehler E (2006) Validity of the brief patient health questionnaire mood scale (PHQ-9) in the general population. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 28(1):71–77
Derogatis LR, Melisaratos N (1983) The brief symptom inventory: an introductory report. Psychol Med 13(03):595–605
de Raaij EJ, Schröder C, Maissan FJ, Pool JJ, Wittink H (2012) Cross-cultural adaptation and measurement properties of the brief illness perception questionnaire-Dutch language version. Man Ther 17(4):330–335
Van Camp YPM, Vrijens B, Abraham I, Van Rompaey B, Elseviers MM (2014) Adherence to phosphate binders in hemodialysis patients: prevalence and determinants. J Nephrol
Hurkmans EJ, Maes S, de Gucht V, Knittle K, Peeters AJ, Ronday HK et al (2010) Motivation as a determinant of physical activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res 62(3):371–377
Harley CR, Frytak JR, Tandon N (2003) Treatment compliance and dosage administration among rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving infliximab, etanercept, or methotrexate. Am J Manag Care 9(6 Suppl):S136–S143
Scheurer D, Choudhry N, Swanton KA, Matlin O, Shrank W (2012) Association between different types of social support and medication adherence. Am J Manag Care 18(12):e461–e467
Borah BJ, Huang X, Zarotsky V, Globe D (2009) Trends in RA patients’ adherence to subcutaneous anti-TNF therapies and costs. Curr Med Res Opin 25(6):1365–1377
de Thurah A, Nørgaard M, Johansen MB, Stengaard-Pedersen K (2010) Methotrexate compliance among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the influence of disease activity, disease duration, and co-morbidity in a 10-year longitudinal study. Scand J Rheumatol 39(3):197–205
Acknowledgments
This research received support from a scientific grant awarded by Merck Sharp & Dohme (MSD) Belgium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have a financial relationship with MSD nor other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work. The authors have full control of all primary data and agree to allow the journal to review their data if requested.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Cuyper, E., De Gucht, V., Maes, S. et al. Determinants of methotrexate adherence in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol 35, 1335–1339 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3182-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3182-4