Abstract
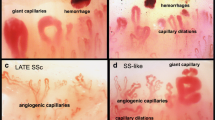
Inflammatory myopathies (IM) are a group of muscle diseases occurring both in children and adults. Nailfold videocapillaroscopy (NVC) alterations are described in IM, but available data are discordant, including differences between polymyositis (PM) and dermatomyositis (DM). The aim of this study was to describe the capillaroscopic differences between PM and DM patients and possible correlation with clinical and serological features. We analyzed 52 unselected patients with IM in a cross-sectional study in a 6-month period. NVC findings of 29 DM and 23 PM patients were compared with those of 52 patients with primary Raynaud’s phenomenon. Tortuosities, capillary loss, enlarged and giant capillaries, microhemorrhages, and ramified capillaries were scored by a semiquantitative rating; disorganization of the vascular array, avascular areas, and scleroderma pattern were scored as presence/absence. Sex, mean age, and mean disease duration were similar in both groups. Disorganization of the vascular array, enlarged and giant capillaries, capillary loss, and scleroderma-like pattern were observed almost only in IM patients. Significant differences were observed between PM and DM with higher frequency and mean score of NVC changes in DM. In DM patients with disease duration ≤6 months (14/29 patients), capillary density was significantly reduced (P = 0.039) and giant capillaries more frequent (P = 0.027), compared with patients with longer disease duration, while a scleroderma pattern tended to be more frequent in patients with a disease duration of less than 6 months. On the contrary, no differences were observed for ramified capillaries with regard to disease duration. Capillaroscopic alterations are identified only in DM patients as expression of diffuse microangiopathy; surprisingly, more severe changes were associated with shorter disease duration, while persistence of ramified capillaries with long-standing disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bohan A, Peter JB (1975) Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med 292:344–348
Bohan A, Peter JB (1975) Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med 292:403–407
Dalakas MC (2010) Inflammatory muscle diseases: a critical review on pathogenesis and therapies. Curr Opin Pharmacol 10:346–352
Dalakas MC (2011) Review: an update on inflammatory and autoimmune myopathies. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37:226–242
Dalakas MC (2012) Pathogenesis and therapies of immune-mediated myopathies. Autoimmun Rev 11:203–206
Dalakas MC, Hohlfeld R (2003) Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Lancet 362:971–982
Marie I, Guillevin L, Menard JF, Hatron PY, Cherin P, Amoura Z et al (2012) Hematological malignancy associated with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Autoimmun Rev 11:615–620
Zahr ZA, Baer AN (2011) Malignancy in myositis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 13:208–215
Wang J, Guo G, Chen G, Wu B, Lu L, Bao L (2013) Meta-analysis of the association of dermatomyositis and polymyositis with cancer. Br J Dermatol 169(Suppl 4):838–847
Maddison P (2001) Cancer types in dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Lancet 357:1443
Sigurgeirsson B, Lindelöf B, Edhag O, Allander E (1992) Risk of cancer in patients with dermatomyositis or polymyositis. A population-based study. N Engl J Med 326:363–367
Koenig M, Joyal F, Fritzler MJ, Roussin A, Abrahamowicz M, Boire G et al (2008) Autoantibodies and microvascular damage are independent predictive factors for the progression of Raynaud’s phenomenon to systemic sclerosis: a twenty-year prospective study of 586 patients, with validation of proposed criteria for early systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 58:3902–3912
Maricq HR, Spencer-Green G, LeRoy EC (1976) Skin capillary abnormalities as indicators of organ involvement in scleroderma (systemic sclerosis), Raynaud’s syndrome and dermatomyositis. Am J Med 61:862–870
Grassi W, De Angelis R (2007) Capillaroscopy: questions and answers. Clin Rheumatol 26:2009–2016
Ingegnoli F, Ardoino I, Boracchi P, Cutolo M, EUSTAR co-authors (2013) Nailfold capillaroscopy in systemic sclerosis: data from the EULAR scleroderma trials and research (EUSTAR) database. Microvasc Res 89:122–128
Cutolo M, Sulli A, Pizzorni C, Accardo S (2000) Nailfold videocapillaroscopy assessment of microvascular damage in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 27:155–160
Lambova SN, Hermann W, Müller-Ladner U (2012) Comparison of qualitative and quantitative analysis of capillaroscopic findings in patients with rheumatic diseases. Rheumatol Int 32:3729–3735
Lee P, Leung FYK, Alderdice C, Armstrong SK (1983) Nailfold capillary microscopy in the connective tissue diseases: a semiquantitative assessment. J Rheumatol 10:930–938
Sulli A, Secchi ME, Pizzorni C, Cutolo M (2008) Scoring the nailfold microvascular changes during the capillaroscopic analysis in systemic sclerosis patients. Ann Rheum Dis 67:885–887
Andrade LE, Gabriel Júnior A, Assad RL, Ferrari AJ, Atra E (1990) Panoramic nailfold capillaroscopy: a new reading method and normal range. Semin Arthritis Rheum 20:21–31
Smith V, Pizzorni C, De Keyser F, Decuman S, Van Praet JT, Deschepper E et al (2010) Reliability of the qualitative and semiquantitative nailfold videocapillaroscopy assessment in a systemic sclerosis cohort: a two-centre study. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1092–1096
Ingegnoli F, Gualtierotti R, Lubatti C, Zahalkova L, Meani L, Boracchi P et al (2009) Feasibility of different capillaroscopic measures for identifying nailfold microvascular alterations. Semin Arthritis Rheum 38:289–295
Selva-O’Callaghan A, Fonollosa-Pla V, Trallero-Araguás E, Martínez-Gómez X, Simeon-Aznar CP, Labrador-Horrillo M et al (2010) Nailfold capillary microscopy in adults with inflammatory myopathy. Semin Arthritis Rheum 39:398–404
Mercer LK, Moore TL, Chinoy H, Murray AK, Vail A, Cooper RG et al (2010) Quantitative nailfold video capillaroscopy in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. Rheumatology 49:1699–1705
Mugii N, Hasegawa M, Matsushita T, Hamaguchi Y, Horie S, Yahata T et al (2011) Association between nail-fold capillary findings and disease activity in dermatomyositis. Rheumatology 50:1091–1098
Szabo N, Csiki Z, Szanto A, Danko K, Szodoray P, Zeher M (2008) Functional and morphological evaluation of hand microcirculation with nailfold capillaroscopy and laser Doppler imaging in Raynaud’s and Sjogren’s syndrome and poly/ dermatomyositis. Scand J Rheumatol 37:23–29
Cox S, Limaye V, Hill C, Blumbergs P, Roberts-Thomson P (2010) Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: diagnostic criteria, classification and epidemiological features. Int J Rheum Dis 13:117–124
Altman DG (1991) Practical statistic for medical research. Chapman et al., London
Leu AJ, Yanar A, Geiger M, Franzeck UK, Bollinger A (1991) Dermatomyositis: diagnostic value of capillary microscopy. [Article in German]. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 121:363–367
De Angelis R, Cutolo M, Gutierrez M, Bertolazzi C, Salaffi F, Grassi W (2012) Different microvascular involvement in dermatomyositis and systemic sclerosis. a preliminary study by a tight videocapillaroscopic assessment. Clin Exp Rheumatol 30:67–70
Klyscz T, Bogenschütz O, Jünger M, Rassner G (1996) Microangiopathic changes and functional disorders of nail fold capillaries in dermatomyositis. [Article in German]. Hautarzt 47:289–293
Leteurtre E, Hachulla E, Janin A, Hatron PY, Brouillard M, Devulder B (1994) Vascular manifestations of dermatomyositis and polymyositis. clinical, capillaroscopic and histological aspects. [Article in French]. Rev Med Interne 15:800–807
Lukasiak B, Vnorowski J (1972) Capillaroscopy studies in dermatomyositis and lupus erythematosus. Z Haut Geschlechtskr [Article in German] 47:509–515
Riccieri V, Vasile R, Macri V, Sciarra I, Stefanantoni K, De Luca N et al (2010) Successful immunosuppressive treatment of dermatomyositis: a nailfold capillaroscopy survey. J Rheumatol 37:443–445
Ganczarczyk ML, Lee P, Armstrong SK (1988) Nailfold capillary microscopy in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheum 31:116–119
Maricq HR, LeRoy EC, D’Angelo WA, Medsger TA Jr, Rodnan GP, Sharp GC et al (1980) Diagnostic potential of in vivo capillary microscopy in scleroderma and related disorders. Arthritis Rheum 23:183–189
Chiricozzi A, Zhang S, Dattola A, Cannizzaro MV, Gabellini M, Chimenti S et al (2012) New insights into the pathogenesis of cutaneous autoimmune disorders. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 26:165–170
Conflict of interest
The authors declares declare that they don’t do not have any financial support or other benefits from commercial sources or any other financial interests which could create a potential conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manfredi, A., Sebastiani, M., Cassone, G. et al. Nailfold capillaroscopic changes in dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Clin Rheumatol 34, 279–284 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2795-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2795-8