Abstract
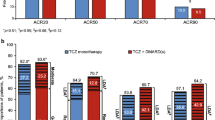
This study aims to investigate the use of biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) as monotherapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in “real world” clinical settings and to compare tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors and tocilizumab monotherapy in terms of efficacy and patient and clinician satisfaction with treatment. This study made use of a retrospective, cohort-19 based study including included data from 254 patients (TNF inhibitors n = 128; tocilizumab n = 126) managed in 30 centers throughout Germany. Efficacy of monotherapy and patient and physician overall satisfaction with treatment were assessed at baseline, 3, and 6 months of monotherapy using a range of measures including Disease Activity Score 28 joint (DAS28), swollen joint count (SJC) and tender joint count (TJC), and visual analogue scales (VAS). Between 18 and 41 % of patients treated with bDMARDs received the agent as monotherapy. Intolerance to DMARDs, contraindications for combination therapy, and comorbidities were the most common reasons for introduction of bDMARD monotherapy. Mean DAS28 (erythrocyte sedimentation rate, ESR) was significantly lower at 3 and 6 months following tocilizumab vs. TNF inhibitors (p ≤ 0.001). Joint counts improved from baseline to month 6 in both groups (SJC −5.1 vs. −3.7 and TJC −5.6 vs. −5.1, for tocilizumab and TNF inhibitors, respectively). Patient as well as physician satisfaction (VAS 100 mm scale) was significantly higher for tocilizumab vs. TNF inhibitors (75.3 vs. 66.8; p = 0.001 and 74.9 vs. 67.1, p = 0.003, respectively). Significantly more patients remained on tocilizumab monotherapy vs. TNF-inhibitor monotherapy (89.7 vs. 75.8 %; p < 0.01). Monotherapy with bDMARDs is common in routine clinical practice. Tocilizumab monotherapy appeared to be superior over TNF-inhibitor monotherapy with respect to DAS28 and drug adherence.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal SK (2011) Core management principles in rheumatoid arthritis to help guide managed care professionals. J Manag Care Pharm 17(9 Suppl B):S03–S08
Gabriel SE, Michaud K (2009) Epidemiological studies in incidence, prevalence, mortality, and comorbidity of the rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther 11:229
Smolen JS, Landewé R, Breedveld FC et al (2010) EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Ann Rheum Dis 69:964–975
DeWitt EM, Lin L, Glick HA, Anstrom KJ, Schulman KA, Reed SD (2009) Pattern and predictors of the initiation of biologic agents for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in the United States: an analysis using a large observational data bank. Clin Ther 31:1871–1880
Yazici Y, Shi N, John A (2008) Utilization of biologic agents in rheumatoid arthritis in the United States: analysis of prescribing patterns in 16,752 newly diagnosed patients and patients new to biologic therapy. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis 66:77–85
Saag KG, Teng GG, Patkar NM et al (2008) American College of Rheumatology 2008 recommendations for the use of nonbiologic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 59:762–784
Listing J, Strangfeld A, Kary S, Rau R, von Hinueber U, Stoyanova-Scholz M, Gromnica-Ihle E, Antoni C, Herzer P, Kekow J, Schneider M, Zink A (2005) Infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologic agents. Arthritis Rheum 52:3403–3412
Soliman MM, Ashcroft DM, Watson KD, Lunt M, Symmons DP, Hyrich KL (2011) Impact of concomitant use of DMARDs on the persistence with anti-TNF therapies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Ann Rheum Dis 70:583–589
Klareskog L, van der Heijde D, de Jager JP et al (2004) Therapeutic effect of the combination of etanercept and methotrexate compared with each treatment alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 363:675–681
Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, Cohen SB, Pavelka K, van Vollenhoven R, Sharp J, Perez JL, Spencer-Green GT (2006) The PREMIER study: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previous methotrexate treatment. Arthritis Rheum 54:26–37
Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM, Tesser JR, Schiff MH, Keystone EC, Genovese MC, Wasko MC, Moreland LW, Weaver AL, Markenson J, Finck BK (2000) A comparison of etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 343:1586–1593
Dougados M, Huizinga T, Sheeran T et al (2011) Tocilizumab (TCZ) plus methotrexate (MTX) does not have superior clinical efficacy to TCZ alone in RA patients with inadequate response to MTX: 24-week results of the ACT-RAY study. Ann Rheum Dis 70(Suppl 3):73
Dougados M, Kissel K, Amital H et al (2011) Double-blind study of tocilizumab plus methotrexate vs. tocilizumab plus placebo in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite prior methotrexate: progression of structural damage, quality of life, and physical function at 24 weeks. Arthritis Rheum 63(Suppl 10):S1032
Gabay C, Emery P, van Vollenhoven R et al (2012) Tocilizumab monotherapy is superior to adalimumab monotherapy in reducing disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: 24 week data from the phase-4 ADACTA trial. Ann Rheum Dis 71(Suppl 3):152
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ et al (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62:2569–2581
van der Heijde DM, van‘t Hof MA, van Riel PL, Theunisse LA, Lubberts EW, van Leeuwen MA, van Rijswijk MH, van de Putte LB (1990) Judging disease activity in clinical practice in rheumatoid arthritis: first step in the development of a disease activity score. Ann Rheum Dis 49:916–920
Prevoo ML, van‘t Hof MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL (1995) Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38:44–48
Wells G, Becker JC, Teng J, Dougados M, Schiff M, Smolen J, Aletaha D, van Riel PL (2009) Validation of the 28-joint Disease Activity Score (DAS28) and European League Against Rheumatism response criteria based on C-reactive protein against disease progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and comparison with the DAS28 based on erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Ann Rheum Dis 68:954–960
Maini RN, Taylor PC, Szechinski J, Pavelka K, Bröll J, Balint G, Emery P, Raemen F, Petersen J, Smolen J, Thomson D, Kishimoto T; CHARISMA Study Group (2006) Double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial of the interleukin-6 receptor antagonist, tocilizumab, in European patients with rheumatoid arthritis who had an incomplete response to methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum 54:2817–2829
Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, Emery P, Close DR, Stevens RM, Shaw T (2004) Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 350:2572–2581
Weinblatt ME, Kremer JM, Bankhurst AD, Bulpitt KJ, Fleischmann RM, Fox RI, Jackson CG, Lange M, Burge DJ (1999) A trial of etanercept, a recombinant tumor necrosis factor receptor:Fc fusion protein, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. N Engl J Med 340:253–259
Kameda H, Ueki Y, Saito K, Nagaoka S, Hidaka T, Atsumi T, Tsukano M, Kasama T, Shiozawa S, Tanaka Y, Takeuchi T (2010) Etanercept (ETN) with methotrexate (MTX) is better than ETN monotherapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite MTX therapy: a randomized trial. Mod Rheumatol 20:531–538
van der Heijde D, Klareskog L, Rodriguez-Valverde V, Codreanu C, Bolosiu H, Melo-Gomes J, Tornero-Molina J, Wajdula J, Pedersen R, Fatenejad S; TEMPO Study Investigators (2006) Comparison of etanercept and methotrexate, alone and combined, in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: two-year clinical and radiographic results from the TEMPO study, a double-blind, randomized trial. Arthritis Rheum 54:1063–1074
Genovese MC, McKay JD, Nasonov EL, Mysler EF, da Silva NA, Alecock E, Woodworth T, Gomez-Reino JJ (2008) Interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab reduces disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: the tocilizumab in combination with traditional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy study. Arthritis Rheum 58:2968–2980
Smolen JS, Beaulieu A, Rubbert-Roth A, Ramos-Remus C, Rovensky J, Alecock E, Woodworth T, Alten R, Investigators OPTION (2008) Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Lancet 371:987–997
Jones G, Sebba A, Gu J, Lowenstein MB, Calvo A, Gomez-Reino JJ, Siri DA, Tomsic M, Alecock E, Woodworth T, Genovese MC (2010) Comparison of tocilizumab monotherapy versus methotrexate monotherapy in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis: the AMBITION study. Ann Rheum Dis 69:88–96
Emery P, Keystone E, Tony HP, Cantagrel A, van Vollenhoven R, Sanchez A, Alecock E, Lee J, Kremer J (2008) IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: results from a 24-week multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 67:1516–1523
Nakashima Y, Kondo M, Harada H, Horiuchi T, Ishinishi T, Jojima H, Kuroda K, Miyahara H, Nagamine R, Nakashima H, Otsuka T, Saikawa I, Shono E, Suematsu E, Tsuru T, Wada K, Iwamoto Y (2010) Clinical evaluation of tocilizumab for patients with active rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-TNF biologics: tocilizumab in combination with methotrexate. Mod Rheumatol 20:343–352
Bergman GJ, Hochberg MC, Boers M, Wintfeld N, Kielhorn A, Jansen JP (2010) Indirect comparison of tocilizumab and other biologic agents in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Semin Arthritis Rheum 39:425–441
Nishimoto N, Yoshizaki K, Maeda K, Kuritani T, Deguchi H, Sato B, Imai N, Suemura M, Kakehi T, Takagi N, Kishimoto T (2003) Toxicity, pharmacokinetics, and dose-finding study of repetitive treatment with the humanized anti-interleukin 6 receptor antibody MRA in rheumatoid arthritis. Phase I/II clinical study. J Rheumatol 30:1426–1435
Fransen J, van Riel PL (2005) The Disease Activity Score and the EULAR response criteria. Clin Exp Rheumatol 23(5 Suppl 39):S93–S99
Felson DT, Smolen JS, Wells G et al (2011) American College of Rheumatology; European League Against Rheumatism. American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism provisional definition of remission in rheumatoid arthritis for clinical trials. Arthritis Rheum 63:573–586
Leffers HC, Ostergaard M, Glintborg B, Krogh NS, Foged H, Tarp U, Lorenzen T, Hansen A, Hansen MS, Jacobsen MS, Dreyer L, Hetland ML (2011) Efficacy of abatacept and tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated in clinical practice: results from the nationwide Danish DANBIO registry. Ann Rheum Dis 70:1216–1222
Yamanaka H, Tanaka Y, Inoue E, Hoshi D, Momohara S, Hanami K, Yunoue N, Saito K, Amano K, Kameda H, Takeuchi T (2011) Efficacy and tolerability of tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis patients seen in daily clinical practice in Japan: results from a retrospective study (REACTION study). Mod Rheumatol 21:122–133
Kawashiri SY, Kawakami A, Iwamoto N, Fujikawa K, Aramaki T, Tamai M, Yamasaki S, Nakamura H, Ueki Y, Migita K, Mizokami A, Origuchi T, Aoyagi K, Eguchi K (2011) Disease activity score 28 may overestimate the remission induction of rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with tocilizumab: comparison with the remission by the clinical disease activity index. Mod Rheumatol 21:365–369
Burmester GR, Feist E, Kellner H, Braun J, Iking-Konert C, Rubbert-Roth A (2011) Effectiveness and safety of the interleukin 6-receptor antagonist tocilizumab after 4 and 24 weeks in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: the first phase IIIb real-life study (TAMARA). Ann Rheum Dis 70:755–759
Backhaus M, Ohrndorf S, Kellner H, Strunk J, Backhaus TM, Hartung W, Sattler H, Albrecht K, Kaufmann J, Becker K, Sörensen H, Meier L, Burmester GR, Schmidt WA (2009) Evaluation of a novel 7-joint ultrasound score in daily rheumatologic practice: a pilot project. Arthritis Rheum 61:1194–1201
Kaufmann J, Seel S, Roske A-E, et al (2010) Comparison of effectiveness (DAS28) of tocilizumab and TNF-a inhibitors in a “real life” setting in rheumatoid arthritis patients inadequately controlled by DMARDs. Arthritis Rheum 62(Suppl.):S22
Zink A, Listing J, Kary S, Rau R, von Hinueber U, Stoyanova-Scholz M, Gromnica-Ihle E, Antoni C, Herzer P, Kekow J, Schneider M, Zink A (2005) Treatment continuation in patients receiving biological agents or conventional DMARD therapy. Ann Rheum Dis 64:1274–1279
Chung C, Mallon C, Spady B et al (2003) Survival analysis of treatment with leflunomide, combination leflunomide/methotrexate, and infliximab for rheumatoid arthritis in routine clinical practice. Arthritis Rheum 48(Suppl 9):S334
Flendrie M, Creemers MC, Welsing PM, den Broeder AA, van Riel PL (2003) Survival during treatment with tumour necrosis factor blocking agents in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 62(Suppl 2):ii30–ii33
Wendling D, Materne GE, Michel F, Lohse A, Lehuede G, Toussirot E, Massol J, Woronoff-Lemsi MC (2005) Infliximab continuation rates in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in everyday practice. Joint Bone Spine 72:309–312
Kristensen LE, Saxne T, Nilsson JA, Geborek P (2006) Impact of concomitant DMARD therapy on adherence to treatment with etanercept and infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis. Results from a six-year observational study in southern Sweden. Arthritis Res Ther 8:R174
Taylor A, Jones G (2011) Biologic monotherapy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical Investigation 1:1291–1300
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the rheumatologists who participated in this study: HJ Hatz, Feldafing; H Kellner, München; I Gürtler, Neuss; MA Vollmer, Mönchengladbach; C Richter, Stuttgart; HP Tony, Würzburg; T Klopsch, Neubrandenburg; K Krüger, München; M Höhle, Hamburg; S Remstedt, Berlin; M Späth, Gräfelfing; WA Biewer, Saarbrücken; G Lorenz, Chemnitz; M Müller, Freiberg; B Heilig, Heidelberg; U Schendel, Bad Münder; CJ Heinmüller, Wuppertal; M Schmitt-Haendle, Bayreuth; K Becker, Blaubeuren; H Fricke-Wagner, Zwickau; K Lüthke, Dresden; PM Aries, Hamburg; T Kupka, Altenburg; C Kühne, Haldensleben; C Binder, München; S Balzer, Bautzen; O Ditrich, Karlsruhe; and HJA Tremel, Hamburg.
Funding
This work was supported by Roche Pharma AG, Germany and Chugai Pharma Marketing Europe Ltd., UK. An employee of Roche Pharma AG is an author on this paper and participated in the design, implementation, and interpretation of the study.
Conflict of interests
EF received honoraria as speaker from Roche, Abbott, Pfizer, and Merck; for participation in advisory boards from Roche and Abbott; and was supported by a grant from Roche. WS received honoraria as speaker from Abbott, Berlin-Chemie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Medac, Merck Pharmaceutical Corporation, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, Roche-Chugai, Smithkline Beecham, and UCB; for participation in advisory boards from Abbott, Berlin-Chemie, Novartis, and Roche-Chugai; and received research grants from Abbott, Actelion, Esaote, GE, Merck Sharp & Dohme, HTA (UK), Novartis, Roche-Chugai. JK received honoraria as speaker from Roche-Chugai, Abbott, Pfizer, and UCB; for participation in clinical studies from Abbott, Pfizer, and Roche; and received research grants from Roche-Chugai. A-ER is an employee of Roche Pharma AG, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Key messages
Monotherapy using biological DMARDs is common in routine clinical practice.
Biological DMARD monotherapy is well tolerated in routine clinical practice.
Tocilizumab monotherapy appeared to be superior over TNF-inhibitor monotherapy with respect to DAS28 and adherence.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaufmann, J., Feist, E., Roske, AE. et al. Monotherapy with tocilizumab or TNF-alpha inhibitors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: efficacy, treatment satisfaction, and persistence in routine clinical practice. Clin Rheumatol 32, 1347–1355 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-013-2281-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-013-2281-8