Summary.
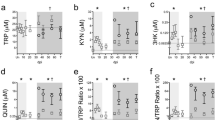
Patients who are infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) frequently present with neurological and psychiatric symptoms. Kynurenic acid (KYNA), an intermediate metabolite of L-kynurenine (L-KYN), is a neuroprotectant and a broad-spectrum antagonist at excitatory amino acid (EAA) receptors. The present study examines the biosynthetic machinery of KYNA in the frontal cortex and cerebellum of 25 HIV-1 and 16 control (CO) patients. We measured the contents of L-KYN and KYNA and the activity of enzymes synthesizing KYNA, kynurenine aminotransferases I and II (KAT I and KAT II). The KYNA level was significantly increased in the frontal cortex (209 ± 38% of CO; p < 0.05) and moderately increased in the cerebellum (164 ± 31% of CO) of HIV-1 brains as compared with controls. The bioprecursor of KYNA, L-KYN, was increased in frontal cortex (188 ± 45% of CO) and cerebellum (151 ± 16% of CO; p < 0.05). The elevated KYNA in frontal cortex correlated with significant increases of KAT I (341 ± 95% of CO; p < 0.05) and KAT II (141 ± 8% of CO; p < 0.05). In the cerebellum, a high KYNA content was in the line with increased KAT I (262 ± 52% of CO; p < 0.05) activity, while KAT II was in a control range (85 ± 12% of CO). This study demonstrates that HIV-1 infection associates with elevated KYNA synthesis in the brain. In contrast to KAT II, KAT I was prominently increased in both brain regions investigated. Differences in neurochemical parameters of KYNA metabolism between frontal cortex and cerebellum suggests selective tissue damage. Drugs which influence the synthesis of the endogenous neuroprotectant KYNA may become useful in the therapy of neuropsychiatric manifestations of HIV-1 infected patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received January 17, 2000; accepted March 22, 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baran, H., Hainfellner, J., Kepplinger, B. et al. Kynurenic acid metabolism in the brain of HIV-1 infected patients. J Neural Transm 107, 1127–1138 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020070026
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020070026