Abstract
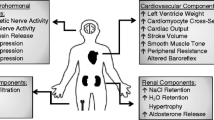
Glucocorticoid-induced hypertension is a common clinical problem that is poorly understood, thus rendering treatment strategies sub-optimal. This form of hypertension has been commonly thought to be mediated by excess sodium and water reabsorption by the renal mineralocorticoid receptor. However, experimental and clinical data in both humans and animal models suggest important roles for the glucocorticoid receptor as well, in both the pathogenesis and maintenance of this hypertension. The glucocorticoid receptor is widely expressed in a number of organ systems relevant to blood pressure regulation, including the kidney, the brain and the vasculature. In vitro studies in isolated kidney tissues as well as in vascular smooth muscle and vascular endothelial cells have attempted to elucidate the molecular physiology of glucocorticoid-induced hypertension, but have generally been limited by the inability to study signaling pathways in an intact organism. More recently, the power of mouse genetics has been employed to examine the tissue-specific contributions of vascular and extra-vascular tissues to this form of hypertension. Here we review recent developments in our understanding of the pathogenesis of glucocorticoid-induced hypertension.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mantero F, Boscaro M (1992) Glucocorticoid-dependent hypertension. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 43:409–413
Baid S, Nieman LK (2004) Glucocorticoid excess and hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 6:493–499
Etxabe J, Vazquez JA (1994) Morbidity and mortality in Cushing's disease: an epidemiological approach. Clin Endocrinol Oxf 40:479–484
Whitworth JA, Mangos GJ, Kelly JJ (2000) Cushing, cortisol, and cardiovascular disease. Hypertension 36:912–916
Sabharwal P, Fishel RS, Breslow MJ (1998) Adrenal insufficiency—an unusual cause of shock in postoperative patients. Endocr Pract 4:387–390
De Wachter E, Vanbesien J, De Schutter I, Malfroot A, De Schepper J (2003) Rapidly developing Cushing syndrome in a 4-year-old patient during combined treatment with itraconazole and inhaled budesonide. Eur J Pediatr 162:488–489
Bertagna X, Bertagna C, Laudat MH, Husson JM, Girard F, Luton JP (1986) Pituitary-adrenal response to the antiglucocorticoid action of RU 486 in Cushing’s syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 63:639–643
Nieman LK, Chrousos GP, Kellner C, Spitz IM, Nisula BC, Cutler GB, Merriam GR, Bardin CW, Loriaux DL (1985) Successful treatment of Cushing's syndrome with the glucocorticoid antagonist RU 486. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 61:536–540
Sartor O, Cutler GB Jr (1996) Mifepristone: treatment of Cushing's syndrome. Clin Obstet Gynecol 39:506–510
Kalimi M (1989) Role of antiglucocorticoid RU 486 on dexamethasone-induced hypertension in rats. Am J Physiol 256:E682–E685
Grunfeld JP, Eloy L, Moura AM, Ganeval D, Ramos-Frendo B, Worcel M (1985) Effects of antiglucocorticoids on glucocorticoid hypertension in the rat. Hypertension 7:292–299
Mangos GJ, Whitworth JA, Williamson PM, Kelly JJ (2003) Glucocorticoids and the kidney. Nephrology (Carlton) 8:267–273
Williamson PM, Kelly JJ, Whitworth JA (1996) Dose-response relationships and mineralocorticoid activity in cortisol-induced hypertension in humans. J Hypertens Suppl 14:S37–S41
Montrella-Waybill M, Clore JN, Schoolwerth AC, Watlington CO (1991) Evidence that high dose cortisol-induced Na+ retention in man is not mediated by the mineralocorticoid receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 72:1060–1066
Li M, Wen C, Fraser T, Whitworth JA (1999) Adrenocorticotrophin-induced hypertension: effects of mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptor antagonism. J Hypertens 17:419–426
Campen TJ, Vaughn DA, Fanestil DD (1983) Mineralo- and glucocorticoid effects on renal excretion of electrolytes. Pflugers Arch 399:93–101
Funder JW, Pearce PT, Myles K, Roy LP (1990) Apparent mineralocorticoid excess, pseudohypoaldosteronism, and urinary electrolyte excretion: toward a redefinition of mineralocorticoid action. FASEB J 4:3234–3238
Muller OG, Parnova RG, Centeno G, Rossier BC, Firsov D, Horisberger JD (2003) Mineralocorticoid effects in the kidney: correlation between alphaENaC, GILZ, and Sgk-1 mRNA expression and urinary excretion of Na+ and K+. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1107–1115
Stewart PM, Corrie JE, Shackleton CH, Edwards CR (1988) Syndrome of apparent mineralocorticoid excess. A defect in the cortisol-cortisone shuttle. J Clin Invest 82:340–349
Todd-Turla KM, Schnermann J, Fejes-Toth G, Naray-Fejes-Toth A, Smart A, Killen PD, Briggs JP (1993) Distribution of mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptor mRNA along the nephron. Am J Physiol 264:F781–F791
Yan K, Kudo A, Hirano H, Watanabe T, Tasaka T, Kataoka S, Nakajima N, Nishibori Y, Shibata T, Kohsaka T, Higashihara E, Tanaka H, Watanabe H, Nagasawa T, Awa S (1999) Subcellular localization of glucocorticoid receptor protein in the human kidney glomerulus. Kidney Int 56:65–73
Baylis C, Handa RK, Sorkin M (1990) Glucocorticoids and control of glomerular filtration rate. Semin Nephrol 10:320–329
Welbourne TC (1990) Glucocorticoid control of ammoniagenesis in the proximal tubule. Semin Nephrol 10:339–349
Rodriguez HJ, Sinha SK, Starling J, Klahr S (1981) Regulation of renal Na+−K+−ATPase in the rat by adrenal steroids. Am J Physiol 241:F186–F195
Freiberg JM, Kinsella J, Sacktor B (1982) Glucocorticoids increase the Na+−H+ exchange and decrease the Na+ gradient-dependent phosphate-uptake systems in renal brush border membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:4932–4936
Kinsella J, Cujdik T, Sacktor B (1984) Na+−H+ exchange activity in renal brush border membrane vesicles in response to metabolic acidosis: the role of glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:630–634
Frick A, Durasin I (1980) Proximal tubular reabsorption of inorganic phosphate in adrenalectomized rats. Pflugers Arch 385:189–192
Welch WJ, Ott CE, Guthrie GP Jr, Kotchen TA (1985) Renin secretion and loop of Henle chloride reabsorption in the adrenalectomized rat. Am J Physiol 249:F596–F602
Doucet A, Hus-Citharel A, Morel F (1986) In vitro stimulation of Na-K-ATPase in rat thick ascending limb by dexamethasone. Am J Physiol 251:F851–F857
Stanton BA (1986) Regulation by adrenal corticosteroids of sodium and potassium transport in loop of Henle and distal tubule of rat kidney. J Clin Invest 78:1612–1620
Naray-Fejes-Toth A, Fejes-Toth G (1990) Glucocorticoid receptors mediate mineralocorticoid-like effects in cultured collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol 259:F672–F678
Naray-Fejes-Toth A, Snyder PM, Fejes-Toth G (2004) The kidney-specific WNK1 isoform is induced by aldosterone and stimulates epithelial sodium channel-mediated Na+ transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:17434–17439
Li C, Li Y, Liu H, Sun Z, Lu J, Zhao Y (2008) Glucocorticoid repression of human with-no-lysine (K) kinase-4 gene expression is mediated by the negative response elements in the promoter. J Mol Endocrinol 40:3–12
Yang CL, Angell J, Mitchell R, Ellison DH (2003) WNK kinases regulate thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransport. J Clin Invest 111:1039–1045
Wilson FH, Disse-Nicodeme S, Choate KA, Ishikawa K, Nelson-Williams C, Desitter I, Gunel M, Milford DV, Lipkin GW, Achard JM, Feely MP, Dussol B, Berland Y, Unwin RJ, Mayan H, Simon DB, Farfel Z, Jeunemaitre X, Lifton RP (2001) Human hypertension caused by mutations in WNK kinases. Science 293:1107–1112
Kahle KT, Wilson FH, Leng Q, Lalioti MD, O'Connell AD, Dong K, Rapson AK, MacGregor GG, Giebisch G, Hebert SC, Lifton RP (2003) WNK4 regulates the balance between renal NaCl reabsorption and K+ secretion [see comment]. Nat Genet 35:372–376
Goodwin JE, Zhang J, Velazquez H, Geller DS (2010) The glucocorticoid receptor in the distal nephron is not necessary for the development or maintenance of dexamethasone-induced hypertension. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 394:266–271
Provencher PH, Saltis J, Funder JW (1995) Glucocorticoids but not mineralocorticoids modulate endothelin-1 and angiotensin II binding in SHR vascular smooth muscle cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 52:219–225
Kornel L, Nelson WA, Manisundaram B, Chigurupati R, Hayashi T (1993) Mechanism of the effects of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids on vascular smooth muscle contractility. Steroids 58:580–587
Tsugita M, Iwasaki Y, Nishiyama M, Taguchi T, Shinahara M, Taniguchi Y, Kambayashi M, Terada Y, Hashimoto K (2008) Differential regulation of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type-1 and −2 gene transcription by proinflammatory cytokines in vascular smooth muscle cells. Life Sci 83:426–432
Wallerath T, Witte K, Schafer SC, Schwarz PM, Prellwitz W, Wohlfart P, Kleinert H, Lehr HA, Lemmer B, Forstermann U (1999) Down-regulation of the expression of endothelial NO synthase is likely to contribute to glucocorticoid-mediated hypertension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13357–13362
Ray KP, Searle N (1997) Glucocorticoid inhibition of cytokine-induced E-selectin promoter activation. Biochem Soc Trans 25:189S
Yang S, Zhang L (2004) Glucocorticoids and vascular reactivity. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2:1–12
Sato A, Suzuki H, Nakazato Y, Shibata H, Inagami T, Saruta T (1994) Increased expression of vascular angiotensin II type 1A receptor gene in glucocorticoid-induced hypertension. J Hypertens 12:511–516
Kornel L, Prancan AV, Kanamarlapudi N, Hynes J, Kuzianik E (1995) Study on the mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced hypertension: glucocorticoids increase transmembrane Ca2+ influx in vascular smooth muscle in vivo. Endocr Res 21:203–210
Molnar GA, Lindschau C, Dubrovska G, Mertens PR, Kirsch T, Quinkler M, Gollasch M, Wresche S, Luft FC, Muller DN, Fiebeler A (2008) Glucocorticoid-related signaling effects in vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension 51:1372–1378
Ong SL, Zhang Y, Sutton M, Whitworth JA (2009) Hemodynamics of dexamethasone-induced hypertension in the rat. Hypertens Res 32:889–894
Cuspidi C, Meani S, Salerno M, Valerio C, Fusi V, Severgnini B, Lonati L, Magrini F, Zanchetti A (2004) Cardiovascular target organ damage in essential hypertensives with or without reproducible nocturnal fall in blood pressure. J Hypertens 22:273–280
Imai Y, Abe K, Sasaki S, Minami N, Munakata M, Nihei M, Sekino H, Yoshinaga K (1989) Exogenous glucocorticoid eliminates or reverses circadian blood pressure variations. J Hypertens 7:113–120
Piovesan A, Panarelli M, Terzolo M, Osella G, Matrella C, Paccotti P, Angeli A (1990) 24-hour profiles of blood pressure and heart rate in Cushing's syndrome: relationship between cortisol and cardiovascular rhythmicities. Chronobiol Int 7:263–265
Fallo F, Fanelli G, Cipolla A, Betterle C, Boscaro M, Sonino N (1994) 24-hour blood pressure profile in Addison's disease. Am J Hypertens 7:1105–1109
Wallerath T, Godecke A, Molojavyi A, Li H, Schrader J, Forstermann U (2004) Dexamethasone lacks effect on blood pressure in mice with a disrupted endothelial NO synthase gene. Nitric Oxide 10:36–41
Mitchell BM, Dorrance AM, Mack EA, Webb RC (2004) Glucocorticoids decrease GTP cyclohydrolase and tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent vasorelaxation through glucocorticoid receptors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 43:8–13
Yudt MR, Cidlowski JA (2002) The glucocorticoid receptor: coding a diversity of proteins and responses through a single gene. Mol Endocrinol 16:1719–1726
Goodwin JE, Zhang J, Geller DS (2008) A critical role for vascular smooth muscle in acute glucocorticoid-induced hypertension. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:1291–1299
Goodwin J, Zhang J, Gonzalez D, Albinsson S, Geller DS (2011) Knockout of the vascular endothelial glucocorticoid receptor abrogates dexamethasone-induced hypertension. J Hypertens 29:1347–1356
Aras-Lopez R, Xavier FE, Ferrer M, Balfagon G (2009) Dexamethasone decreases neuronal nitric oxide release in mesenteric arteries from hypertensive rats through decreased protein kinase C activation. Clin Sci (Lond) 117:305–312
Rask E, Olsson T, Soderberg S, Andrew R, Livingstone DE, Johnson O, Walker BR (2001) Tissue-specific dysregulation of cortisol metabolism in human obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:1418–1421
Masuzaki H, Paterson J, Shinyama H, Morton NM, Mullins JJ, Seckl JR, Flier JS (2001) A transgenic model of visceral obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Science 294:2166–2170
Paterson JM, Morton NM, Fievet C, Kenyon CJ, Holmes MC, Staels B, Seckl JR, Mullins JJ (2004) Metabolic syndrome without obesity: hepatic overexpression of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:7088–7093
Zhang J, Ge R, Matte-Martone C, Goodwin J, Shlomchik WD, Mamula MJ, Kooshkabadi A, Hardy MP, Geller D (2009) Characterization of a novel gain of function glucocorticoid receptor knock-in mouse. J Biol Chem 284:6249–6259
Krug AW, Ehrhart-Bornstein M (2008) Adrenocortical dysfunction in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Horm Metab Res 40:515–517
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goodwin, J.E., Geller, D.S. Glucocorticoid-induced hypertension. Pediatr Nephrol 27, 1059–1066 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-011-1928-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-011-1928-4