Abstract
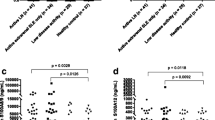
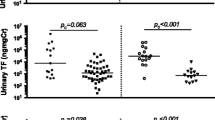
We hypothesized that neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) is an early predictive biomarker of disease activity in lupus nephritis. NGAL in serial plasma (PNGAL) and urine (UNGAL) samples was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in 85 participants with pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus (pSLE), healthy children (n = 50), and children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) (n = 30). Disease activity was measured by the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI). Plasma and urinary NGAL were significantly increased in subjects with pSLE compared with those with JIA or with healthy controls (all p < 0.03), and unrelated to subjects’ age, weight, or height. Plasma and urinary NGAL were stable in pSLE subjects with unchanged disease activity. The pSLE subjects with worsening global or renal disease activity had a mean ± standard error (SE) increase of UNGAL (in ng/ml) of 11.5 ± 6.4 or 36.6 ± 12.1 (p < 0.01), corresponding to a 156% or 380% increase, respectively. PNGAL increased with worsening disease but to a much lesser degree than UNGAL [global disease activity (mean ± SE): 7.3 ± 6.2 or 21%; renal disease activity: 20.2 ± 6.0 or 51%; both p = not significant]. In conclusion, NGAL in urine but not in plasma represents a novel biomarker for renal disease activity in pSLE.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
Ho A, Barr SG, Magder LS, Petri M (2001) A decrease in complement is associated with increased renal and hematologic activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 44:2350–2357
Schiffenbauer J, Hahn B, Weisman MH, Simon LS (2004) Biomarkers, surrogate markers, and design of clinical trials of new therapies for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 50:2415–2422
Schmidt-Ott KM, Mori K, Li JY, Kalandadze A, Cohen DJ, Devarajan P, Barasch J (2007) Dual action of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:407–413
Supavekin S, Zhang W, Kucherlapati R, Kaskel FJ, Moore LC, Devarajan P (2003) Differential gene expression following early renal ischemia/reperfusion. Kidney Int 63:1714–1724
Mishra J, Ma Q, Prada A, Mitsnefes M, Zahedi K, Yang J, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2003) Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2534–2543
Mishra J, Mori K, Ma Q, Kelly C, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2004) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a novel early urinary biomarker for cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Am J Nephrol 24:307–315
Mishra J, Mori K, Ma Q, Kelly C, Yang J, Mitsnefes M, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2004) Amelioration of ischemic acute renal injury by neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:3073–3082
Devarajan P, Mishra J, Supavekin S, Patterson LT, Steven Potter S (2003) Gene expression in early ischemic renal injury: clues towards pathogenesis, biomarker discovery, and novel therapeutics. Mol Genet Metab 80:365–376
Devarajan P (2005) Cellular and molecular derangements in acute tubular necrosis. Curr Opin Pediatr 17:193–199
Nguyen MT, Ross GF, Dent CL, Devarajan P (2005) Early prediction of acute renal injury using urinary proteomics. Am J Nephrol 25:318–326
Mishra J, Ma Q, Kelly K, Mitsnefes M, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2006) Kidney NGAL is a novel earl marker of acute injury following transplantation. Pediatr Nephrol 21:856–863
Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, Ruff SM, Zahedi K, Shao M, Bean J, Mori K, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2005) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet 365:1231–1238
Brunner HI, Mueller M, Rutherford C, Passo MH, Witte D, Grom A, Mishra J, Devarajan P (2006) Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker of nephritis in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 54:2577–2584
Biezeveld MH, van Mierlo G, Lutter R, Kuipers IM, Dekker T, Hack CE, Newburger JW, Kuijpers TW (2005) Sustained activation of neutrophils in the course of Kawasaki disease: an association with matrix metalloproteinases. Clin Exp Immunol 141:183–188
Lim R, Ahmed N, Borregaard N, Riley C, Wafai R, Thompson EW, Quinn MA, Rice GE (2007) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) an early–screening biomarker for ovarian cancer: NGAL is associated with epidermal growth factor-induced epithelio-mesenchymal transition. Int J Cancer 120:2426–2434
Bachorzewska-Gajewska H, Malyszko J, Sitniewska E, Malyszko JS, Dobrzycki S (2007) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) correlations with cystatin C, serum creatinine and eGFR in patients with normal serum creatinine undergoing coronary angiography. Nephrol Dial Transplant 22:295–296
Ohlsson S, Wieslander J, Segelmark M (2003) Increased circulating levels of proteinase 3 in patients with anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic autoantibodies-associated systemic vasculitis in remission. Clin Exp Immunol 131:528–535
Petty RE, Southwood TR, Baum J, Bhettay E, Glass DN, Manners P, Maldonado-Cocco J, Suarez-Almazor M, Orozco-Alcala J, Prieur AM (1998) Revision of the proposed classification criteria for juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Durban, 1997. J Rheumatol 25:1991–1994
Gladman DD, Ibanez D, Urowitz MB (2002) Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J Rheumatol 29:288–291
Weening JJ, D’Agati VD, Schwartz MM, Seshan SV, Alpers CE, Appel GB, Balow JE, Bruijn JA, Cook T, Ferrario F, Fogo AB, Ginzler EM, Hebert L, Hill G, Hill P, Jennette JC, Kong NC, Lesavre P, Lockshin M, Looi LM, Makino H, Moura LA, Nagata M (2004) The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int 65:521–530
Churg J, Bernstein J, Glassock RJ (1995) Renal disease: classification and atlas of glomerular diseases, 2nd edn. Igaku-Shoin, New York, p 541, p xvi
Giannini EH, Ruperto N, Ravelli A, Lovell DJ, Felson DT, Martini A (1997) Preliminary definition of improvement in juvenile arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 40:1202–1209
Pitashny M, Schwartz N, Qing X, Hojaili B, Aranow C, Mackay M, Putterman C (2007) Urinary lipocalin-2 is associated with renal disease activity in human lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum 56:1894–1903
Devarajan P (2007) Emerging biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Contrib Nephrol 156:203–212
Wagener G, Jan M, Kim M, Mori K, Barasch JM, Sladen RN, Lee HT (2006) Association between increases in urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and acute renal dysfunction after adult cardiac surgery. Anesthesiology 105:485–491
Parikh CR, Jani A, Mishra J, Ma Q, Kelly C, Barasch J, Edelstein CL, Devarajan P (2006) Urine NGAL and IL-18 are predictive biomarkers for delayed graft function following kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 6:1639–1645
Hemdahl AL, Gabrielsen A, Zhu C, Eriksson P, Hedin U, Kastrup J, Thoren P, Hansson GK (2006) Expression of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:136–142
Mori K, Lee HT, Rapoport D, Drexler IR, Foster K, Yang J, Schmidt-Ott KM, Chen X, Li JY, Weiss S, Mishra J, Cheema FH, Markowitz G, Suganami T, Sawai K, Mukoyama M, Kunis C, D’Agati V, Devarajan P, Barasch J (2005) Endocytic delivery of lipocalin-siderophore-iron complex rescues the kidney from ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest 115:610–621
Hay EM, Bacon PA, Gordon C, Isenberg DA, Maddison P, Snaith ML, Symmons DP, Viner N, Zoma A (1993) The BILAG index: a reliable and valid instrument for measuring clinical disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Q J Med 86:447–458
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by clinical research grant NIAMS P60 AR47784. Dr. Brunner is supported by a grant from the Alliance for Lupus Research and the CCHMC Translational Research Initiative. Dr. Devarajan is supported by grants from the NIH/NIDDK (RO1 DK53289, P50 DK52612, R21 DK060163). Dr. Wiers is supported by T32 AR007594 and the NIH Loan Repayment Program. We are indebted to our clinical coordinators Jamie Meyer-Eaton and Shannen Nelson for their assistance, Lukasz Itert for the data management, the NIAMS Tissue Repository (director: Susan Thompson; AR047363) for the sample management, Qing Ma for her technological support, and to our patients and families for their participation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, M., Wiers, K.M., Klein-Gitelman, M.S. et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker of disease activity in pediatric lupus nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 23, 403–412 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-007-0685-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-007-0685-x