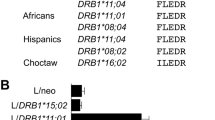
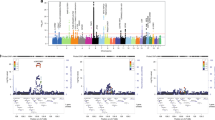
Abstract
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a severe connective tissue disorder characterized by extensive fibrosis, vascular damage, and autoimmune events. During the last years, the number of genetic markers convincingly associated with SSc has exponentially increased. In this report, we aim to offer an updated review of the classical and novel genetic associations with SSc, analyzing the firmest and replicated signals within HLA and non-HLA genes, identified by both candidate gene and genome-wide association (GWA) studies. We will also provide an insight into the future perspectives and approaches that might shed more light into the complex genetic background underlying SSc. In spite of the remarkable advance in the field of SSc genetics during the last decade, the use of the new genetic technologies such as next generation sequencing (NGS), as well as the deep phenotyping of the study cohorts, to fully characterize the genetic component of this disease is imperative.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson P, Paterson HF, Hall A (1992) Intracellular localization of the P21rho proteins. J Cell Biol 119:617–627
Anaya JM et al (2011) Evaluation of genetic association between an ITGAM non-synonymous SNP (rs1143679) and multiple autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev
Alkan C, Coe BP, Eichler EE (2011) Genome structural variation discovery and genotyping. Nat Rev Genet 12:363–376
Allanore Y et al (2011) Genome-wide scan identifies TNIP1, PSORS1C1, and RHOB as novel risk loci for systemic sclerosis. PLoS Genet 7:e1002091
Arnett FC et al (1996) Increased prevalence of systemic sclerosis in a Native American tribe in Oklahoma. Association with an Amerindian HLA haplotype. Arthritis Rheum 39:1362–1370
Arnett FC et al (2001) Familial occurrence frequencies and relative risks for systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) in three United States cohorts. Arthritis Rheum 44:1359–1362
Arnett FC et al (2010) Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II alleles, haplotypes and epitopes which confer susceptibility or protection in systemic sclerosis: analyses in 1300 Caucasian, African-American and Hispanic cases and 1000 controls. Ann Rheum Dis 69:822–827
Assassi S et al (2007) Clinical, immunologic, and genetic features of familial systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 56:2031–2037
Assassi S et al (2010) Systemic sclerosis and lupus: points in an interferon-mediated continuum. Arthritis Rheum 62:589–598
Avouac J et al (2010) Associated autoimmune diseases in systemic sclerosis define a subset of patients with milder disease: results from 2 large cohorts of European Caucasian patients. J Rheumatol 37:608–614
Avouac J et al (2011) Inactivation of the transcription factor STAT-4 prevents inflammation-driven fibrosis in animal models of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 63:800–809
Balada E et al (2006) Lack of association of the PTPN22 gene polymorphism R620 W with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 24:321–324
Bansal V et al (2010) Statistical analysis strategies for association studies involving rare variants. Nat Rev Genet 11:773–785
Beretta L et al (2007) Interleukin-1 gene complex polymorphisms in systemic sclerosis patients with severe restrictive lung physiology. Hum Immunol 68:603–609
Beretta L, Rueda B, Marchini M, Santaniello A, Simeón CP, Fonollosa V, Caronni M, Rios R, Castellvi I, Rodriguez L, Spanish systemic sclerosis group, Moreno A, López-Nevot MA, Escalera A, González-Escribano MF, Martin J, Scorza R (2011) A large association study confirms the role of the HLA-DRB1*1104-DQA1*0501-DQB1*0301 haplotype in systemic sclerosis genetic predisposition in European populations. Rheumatology (Oxford) (in press)
Borowiec M et al (2009) Mutations at the BLK locus linked to maturity onset diabetes of the young and beta-cell dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:14460–14465
Bossini-Castillo L et al (2011a) Confirmation of association of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor gene with systemic sclerosis in a large European population. Rheumatology (Oxford) 50:1976–1981
Bossini-Castillo L et al (2011b) A replication study confirms the association of TNFSF4 (OX40L) polymorphisms with systemic sclerosis in a large European cohort. Ann Rheum Dis 70:638–641
Broen J et al (2011) A rare polymorphism in Toll Like Receptor 2 is associated with systemic sclerosis phenotype and increases production of inflammatory mediators. Arthritis Rheum (in press)
Brooks WH et al (2010) Epigenetics and autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 34:J207–J219
Calandra T, Roger T (2003) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: a regulator of innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 3:791–800
Call ME, Wucherpfennig KW (2004) Molecular mechanisms for the assembly of the T cell receptor-CD3 complex. Mol Immunol 40:1295–1305
Caramaschi P et al (2007) Coexistence of systemic sclerosis with other autoimmune diseases. Rheumatol Int 27:407–410
Carmona FD et al (2011) Association of a non-synonymous functional variant of the ITGAM gene with systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 70:2050–2052
Carmona FD et al (2012) Novel identification of the IRF7 region as an anticentromere autoantibody propensity locus in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 71:114–119
Chang YK et al (2009) Association of BANK1 and TNFSF4 with systemic lupus erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese. Genes Immun 10:414–420
Cheung YH, Watkinson J, Anastassiou D (2011) Conditional meta-analysis stratifying on detailed HLA genotypes identifies a novel type 1 diabetes locus around TCF19 in the MHC. Hum Genet 129:161–176
Cordell HJ (2009) Detecting gene–gene interactions that underlie human diseases. Nat Rev Genet 10:392–404
Coustet B et al (2011a) Association study of ITGAM, ITGAX, and CD58 autoimmune risk loci in systemic sclerosis: results from 2 large European Caucasian cohorts. J Rheumatol 38:1033–1038
Coustet B et al (2011b) C8orf13-BLK is a genetic risk locus for systemic sclerosis and has additive effects with BANK1: results from a large french cohort and meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum 63:2091–2096
Cunninghame Graham DS et al (2008) Polymorphism at the TNF superfamily gene TNFSF4 confers susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 40:83–89
Davey JW et al (2011) Genome-wide genetic marker discovery and genotyping using next-generation sequencing. Nat Rev Genet 12:499–510
de Bakker PI et al (2006) A high-resolution HLA and SNP haplotype map for disease association studies in the extended human MHC. Nat Genet 38:1166–1172
Delgado-Vega A et al (2010) Recent findings on genetics of systemic autoimmune diseases. Curr Opin Immunol 22:698–705
Diaz-Gallo LM et al (2011) Analysis of the influence of PTPN22 gene polymorphisms in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 70:454–462
Dieude P et al (2008) The PTPN22 620 W allele confers susceptibility to systemic sclerosis: findings of a large case-control study of European Caucasians and a meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum 58:2183–2188
Dieude P et al (2009a) Association between the IRF5 rs2004640 functional polymorphism and systemic sclerosis: a new perspective for pulmonary fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum 60:225–233
Dieude P et al (2009b) STAT4 is a genetic risk factor for systemic sclerosis having additive effects with IRF5 on disease susceptibility and related pulmonary fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum 60:2472–2479
Dieude P et al (2009c) BANK1 is a genetic risk factor for diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis and has additive effects with IRF5 and STAT4. Arthritis Rheum 60:3447–3454
Dieude P et al (2010a) Phenotype-haplotype correlation of IRF5 in systemic sclerosis: role of 2 haplotypes in disease severity. J Rheumatol 37:987–992
Dieude P et al (2010b) Association of the TNFAIP3 rs5029939 variant with systemic sclerosis in the European Caucasian population. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1958–1964
Dieude P et al (2011a) Independent replication establishes the CD247 gene as a genetic systemic sclerosis susceptibility factor. Ann Rheum Dis 70:1695–1696
Dieude P et al (2011b) Association of the CD226 Ser(307) variant with systemic sclerosis: evidence of a contribution of costimulation pathways in systemic sclerosis pathogenesis. Arthritis Rheum 63:1097–1105
Dieude P et al (2011c) NLRP1 influences the systemic sclerosis phenotype: a new clue for the contribution of innate immunity in systemic sclerosis-related fibrosing alveolitis pathogenesis. Ann Rheum Dis 70:668–674
Dymecki SM, Niederhuber JE, Desiderio SV (1990) Specific expression of a tyrosine kinase gene, blk, in B lymphoid cells. Science 247:332–336
Fagerholm SC et al (2006) alpha-Chain phosphorylation of the human leukocyte CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1) integrin is pivotal for integrin activation to bind ICAMs and leukocyte extravasation. Blood 108:3379–3386
Fanning GC et al (1998) HLA associations in three mutually exclusive autoantibody subgroups in UK systemic sclerosis patients. Br J Rheumatol 37:201–207
Feghali-Bostwick C, Medsger TA Jr, Wright TM (2003) Analysis of systemic sclerosis in twins reveals low concordance for disease and high concordance for the presence of antinuclear antibodies. Arthritis Rheum 48:1956–1963
Festen EA et al (2011) A meta-analysis of genome-wide association scans identifies IL18RAP, PTPN2, TAGAP, and PUS10 as shared risk loci for Crohn’s disease and celiac disease. PLoS Genet 7:e1001283
Fonseca C et al (2006) Endothelin axis polymorphisms in patients with scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum 54:3034–3042
Frazer KA et al (2009) Human genetic variation and its contribution to complex traits. Nat Rev Genet 10:241–251
Gabrielli A, Avvedimento EV, Krieg T (2009) Scleroderma. N Engl J Med 360:1989–2003
Gateva V et al (2009) A large-scale replication study identifies TNIP1, PRDM1, JAZF1, UHRF1BP1 and IL10 as risk loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 41:1228–1233
Gilchrist FC et al (2001) Class II HLA associations with autoantibodies in scleroderma: a highly significant role for HLA-DP. Genes Immun 2:76–81
Gorlova O et al (2011) Identification of novel genetic markers associated with clinical phenotypes of systemic sclerosis through a genome-wide association strategy. PLoS Genet 7:e1002178
Gough MJ, Weinberg AD (2009) OX40 (CD134) and OX40L. Adv Exp Med Biol 647:94–107
Gourh P et al (2006) Association of the PTPN22 R620 W polymorphism with anti-topoisomerase I- and anticentromere antibody-positive systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 54:3945–3953
Gourh P et al (2009) Polymorphisms in TBX21 and STAT4 increase the risk of systemic sclerosis: evidence of possible gene–gene interaction and alterations in Th1/Th2 cytokines. Arthritis Rheum 60:3794–3806
Gourh P et al (2010a) Association of the C8orf13-BLK region with systemic sclerosis in North-American and European populations. J Autoimmun 34:155–162
Gourh P et al (2010b) Association of TNFSF4 (OX40L) polymorphisms with susceptibility to systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 69:550–555
Graham RR et al (2006) A common haplotype of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) regulates splicing and expression and is associated with increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 38:550–555
Graham RR et al (2007) Three functional variants of IFN regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) define risk and protective haplotypes for human lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:6758–6763
Gregersen PK, Bucala R (2003) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor, MIF alleles, and the genetics of inflammatory disorders: incorporating disease outcome into the definition of phenotype. Arthritis Rheum 48:1171–1176
Gregersen PK, Silver J, Winchester RJ (1987) The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 30:1205–1213
Guo L et al (2009) Replication of the BANK1 genetic association with systemic lupus erythematosus in a European-derived population. Genes Immun 10:531–538
Hall JC, Rosen A (2010) Type I interferons: crucial participants in disease amplification in autoimmunity. Nat Rev Rheumatol 6:40–49
Hom G et al (2008) Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13-BLK and ITGAM-ITGAX. N Engl J Med 358:900–909
Hudson KL (2011) Genomics, health care, and society. N Engl J Med 365:1033–1041
Hudson M et al (2008) Polyautoimmunity and familial autoimmunity in systemic sclerosis. J Autoimmun 31:156–159
Hummers LK (2010) The current state of biomarkers in systemic sclerosis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 12:34–39
Invernizzi P (2009) Future directions in genetic for autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun 33:1–2
Islam KB et al (1995) Molecular cloning, characterization, and chromosomal localization of a human lymphoid tyrosine kinase related to murine Blk. J Immunol 154:1265–1272
Ito I et al (2009) Association of a functional polymorphism in the IRF5 region with systemic sclerosis in a Japanese population. Arthritis Rheum 60:1845–1850
Ito I et al (2010) Association of the FAM167A-BLK region with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 62:890–895
Johnson SR et al (2011) Validation of potential classification criteria for systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) (in press)
Kawaguchi Y et al (2006) NOS2 polymorphisms associated with the susceptibility to pulmonary arterial hypertension with systemic sclerosis: contribution to the transcriptional activity. Arthritis Res Ther 8:R104
Kozyrev SV et al (2008) Functional variants in the B-cell gene BANK1 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 40:211–216
Kuwana M et al (1995) HLA class II genes associated with anticentromere antibody in Japanese patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Ann Rheum Dis 54:983–987
Kuwana M et al (1999) Association of human leukocyte antigen class II genes with autoantibody profiles, but not with disease susceptibility in Japanese patients with systemic sclerosis. Intern Med 38:336–344
Laird RM, Laky K, Hayes SM (2010) Unexpected role for the B cell-specific Src family kinase B lymphoid kinase in the development of IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells. J Immunol 185:6518–6527
Lee YH et al (2011) The association between the PTPN22 C1858T polymorphism and systemic sclerosis: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep (in press)
Lei W et al (2009) Abnormal DNA methylation in CD4 + T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, and dermatomyositis. Scand J Rheumatol 38:369–374
LeRoy EC et al (1988) Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol 15:202–205
Lim CP, Cao X (2006) Structure, function, and regulation of STAT proteins. Mol Biosyst 2:536–550
Manetti M et al (2009) Association between a stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1/CXCL12) gene polymorphism and microvascular disease in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 68:408–411
Manetti M et al (2010) Association of a functional polymorphism in the matrix metalloproteinase-12 promoter region with systemic sclerosis in an Italian population. J Rheumatol 37:1852–1857
Manetti M et al (2011) A genetic variation located in the promoter region of the UPAR (CD87) gene is associated with the vascular complications of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 63:247–256
Manolio TA et al (2009) Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature 461(7265):747–753
Martin JE, Carmona FD, Broen JC, Simeón CP, Vonk MC, Carreira P, Ríos-Fernández R, Espinosa G, Vicente-Rabaneda E et al (2011) The autoimmune disease-associated IL2RA locus is involved in the clinical manifestations of systemic sclerosis. Genes and Immunity (in press)
Martinez A et al (2008) Association of the STAT4 gene with increased susceptibility for some immune-mediated diseases. Arthritis Rheum 58:2598–2602
Mattuzzi S et al (2007) Association of polymorphisms in the IL1B and IL2 genes with susceptibility and severity of systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 34:997–1004
Mayes MD et al (2003) Prevalence, incidence, survival, and disease characteristics of systemic sclerosis in a large US population. Arthritis Rheum 48:2246–2255
McHugh NJ et al (1994) Anti-centromere antibodies (ACA) in systemic sclerosis patients and their relatives: a serological and HLA study. Clin Exp Immunol 96:267–274
Monsuur AJ et al (2008) Effective detection of human leukocyte antigen risk alleles in celiac disease using tag single nucleotide polymorphisms. PLoS One 3:e2270
Mora GF (2009) Systemic sclerosis: environmental factors. J Rheumatol 36:2383–2396
Mukasa R et al (2010) Epigenetic instability of cytokine and transcription factor gene loci underlies plasticity of the T helper 17 cell lineage. Immunity 32:616–627
Muller-Hilke B (2009) HLA class II and autoimmunity: epitope selection vs differential expression. Acta Histochem 111:379–381
Mustelin T et al (2003) Role of protein tyrosine phosphatases in T cell activation. Immunol Rev 191:139–147
Nair RP et al (2000) Localization of psoriasis-susceptibility locus PSORS1 to a 60-kb interval telomeric to HLA-C. Am J Hum Genet 66:1833–1844
Nath SK et al (2008) A nonsynonymous functional variant in integrin-alpha(M) (encoded by ITGAM) is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 40:152–154
Nordmark G et al (2011) Association of EBF1, FAM167A(C8orf13)-BLK and TNFSF4 gene variants with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Genes Immun 12:100–109
O’Connell RM et al (2010) Physiological and pathological roles for microRNAs in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 10:111–122
Orozco G et al (2009) Study of functional variants of the BANK1 gene in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 60:372–379
Orozco G et al (2011) Study of the common genetic background for rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 70:463–468
Orru V et al (2009) A loss-of-function variant of PTPN22 is associated with reduced risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Mol Genet 18:569–579
O’Shea JJ (1997) Jaks, STATs, cytokine signal transduction, and immunoregulation: are we there yet? Immunity 7:1–11
Radstake TR et al (2010) Genome-wide association study of systemic sclerosis identifies CD247 as a new susceptibility locus. Nat Genet 42:426–429
Rahman P et al (2005) Association of SEEK1 and psoriatic arthritis in two distinct Canadian populations. Ann Rheum Dis 64:1370–1372
Rakyan VK et al (2011) Epigenome-wide association studies for common human diseases. Nat Rev Genet 12:529–541
Ramos-Casals M et al (2010) Targeted therapy for systemic sclerosis: how close are we? Nat Rev Rheumatol 6:269–278
Rands AL et al (2000) MHC class II associations with autoantibody and T cell immune responses to the scleroderma autoantigen topoisomerase I. J Autoimmun 15:451–458
Ranque B, Mouthon L (2010) Geoepidemiology of systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev 9:A311–A318
Raychaudhuri S et al (2008) Common variants at CD40 and other loci confer risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet 40:1216–1223
Reveille JD (2003) Ethnicity and race and systemic sclerosis: how it affects susceptibility, severity, antibody genetics, and clinical manifestations. Curr Rheumatol Rep 5:160–167
Rubtsov AV et al (2010) Genetic and hormonal factors in female-biased autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 9:494–498
Rueda B et al (2009) The STAT4 gene influences the genetic predisposition to systemic sclerosis phenotype. Hum Mol Genet 18:2071–2077
Rueda B et al (2010) BANK1 functional variants are associated with susceptibility to diffuse systemic sclerosis in Caucasians. Ann Rheum Dis 69:700–705
Saijo K et al (2003) Essential role of Src-family protein tyrosine kinases in NF-kappaB activation during B cell development. Nat Immunol 4:274–279
Sigurdsson S et al (2005) Polymorphisms in the tyrosine kinase 2 and interferon regulatory factor 5 genes are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Hum Genet 76:528–537
Simeon CP et al (2009) Association of HLA class II genes with systemic sclerosis in Spanish patients. J Rheumatol 36:2733–2736
Svyryd Y et al (2010) X chromosome monosomy in primary and overlapping autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev (in press)
Tavares RM et al (2010) The ubiquitin modifying enzyme A20 restricts B cell survival and prevents autoimmunity. Immunity 33:181–191
Thomas D (2010) Gene–environment-wide association studies: emerging approaches. Nat Rev Genet 11:259–272
Tretter T et al (2003) Mimicry of pre-B cell receptor signaling by activation of the tyrosine kinase Blk. J Exp Med 198:1863–1873
Tsuchiya N et al (2009) Association of STAT4 polymorphism with systemic sclerosis in a Japanese population. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1375–1376
Uz E et al (2008) Skewed X-chromosome inactivation in scleroderma. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 34:352–355
Valdes AM, Thomson G (2009) Several loci in the HLA class III region are associated with T1D risk after adjusting for DRB1-DQB1. Diabetes Obes Metab 11(Suppl 1):46–52
Vereecke L, Beyaert R, van Loo G (2009) The ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 (TNFAIP3) is a central regulator of immunopathology. Trends Immunol 30:383–391
Vettori S et al (2010) The beta-fibrinogen -455 G > A gene polymorphism is associated with peripheral vascular injury in systemic sclerosis patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol 28:923–924
Voskuhl R (2011) Sex differences in autoimmune diseases. Biol Sex Differ 2:1
Wang X et al (2005) Positional identification of TNFSF4, encoding OX40 ligand, as a gene that influences atherosclerosis susceptibility. Nat Genet 37:365–372
Wang Y, Fan PS, Kahaleh B (2006) Association between enhanced type I collagen expression and epigenetic repression of the FLI1 gene in scleroderma fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum 54:2271–2279
Watford WT et al (2004) Signaling by IL-12 and IL-23 and the immunoregulatory roles of STAT4. Immunol Rev 202:139–156
Wipff J et al (2007) Association between an endoglin gene polymorphism and systemic sclerosis-related pulmonary arterial hypertension. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46:622–625
Wipff J et al (2009) Association of hypoxia-inducible factor 1A (HIF1A) gene polymorphisms with systemic sclerosis in a French European Caucasian population. Scand J Rheumatol 38:291–294
Wipff J et al (2010) Association of a KCNA5 gene polymorphism with systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension in the European Caucasian population. Arthritis Rheum 62:3093–3100
Wu SP et al (2006) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promoter polymorphisms and the clinical expression of scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum 54:3661–3669
Yokoyama K et al (2002) BANK regulates BCR-induced calcium mobilization by promoting tyrosine phosphorylation of IP(3) receptor. EMBO J 21:83–92
Zhang F et al (2009) Copy number variation in human health, disease, and evolution. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 10:451–481
Zhernakova A et al (2011) Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies in celiac disease and rheumatoid arthritis identifies fourteen non-HLA shared loci. PLoS Genet 7:e1002004
Zhou X et al (2009) HLA-DPB1 and DPB2 are genetic loci for systemic sclerosis: a genome-wide association study in Koreans with replication in North Americans. Arthritis Rheum 60:3807–3814
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martín, J.E., Bossini-Castillo, L. & Martín, J. Unraveling the genetic component of systemic sclerosis. Hum Genet 131, 1023–1037 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-011-1137-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-011-1137-z