Abstract
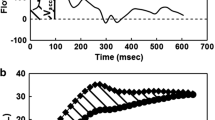
Goals of our study were to compare the pulmonary hemodynamics between healthy volunteers and patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and correlate MR flow measurements with echocardiography. Twenty-five patients with PAH and 25 volunteers were examined at 1.5 T. Phase-contrast flow measurements were performed in the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk, resulting in the following parameters: peak velocity (cm/s), average blood flow (l/min), time to peak velocity (ms), velocity rise gradient and pulmonary distensibility (cm2). The bronchosystemic shunt was calculated. In PAH patients transthoracic echocardiography and right-heart catheterization (RHC) served as the gold standard. In comparison to volunteers, the PAH patients showed significantly reduced pulmonary velocities (P = 0.002), blood flow (P = 0.002) and pulmonary distensibility (P = 0.008). In patients, the time to peak velocity was shorter (P<0.001), and the velocity rise gradient was steeper (P = 0.002) than in volunteers. While in volunteers the peak velocity in the aorta was reached earlier, it was the reverse in patients. Patients showed a significant bronchosystemic shunt (P = 0.01). No meaningful correlation was found between MRI measurements and echocardiography or RHC. MRI is a feasible technique for the differentiation between PAH and volunteers. Further studies have to be conducted for the absolute calculation of pressure estimates.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Simonneau G, Galie N, Rubin LJ, Langleben D, Seeger W, Domenighetti G, Gibbs S, Lebrec D, Speich R, Beghetti M, Rich S, Fishman A (2004) Clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:5S–12S
Barst RJ, McGoon M, Torbicki A, Sitbon O, Krowka MJ, Olschewski H, Gaine S (2004) Diagnosis and differential assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:40S–47S
Kitabatake A, Inoue M, Asao M (1983) Noninvasive evaluation of pulmonary hypertension by a pulsed Doppler technique. Circulation 68:302–309
Ley S, Kreitner K-F, Fink C, Heussel CP, Borst MM, Kauczor H-U (2004) Assessment of pulmonary hypertension by CT and MR imaging. Eur Radiol 14:359–368
Ley S, Fink C, Zaporozhan J, Borst MM, Meyer FJ, Puderbach M, Eichinger M, Plathow C, Grunig E, Kreitner KF, Kauczor HU (2005) Value of high spatial and high temporal resolution magnetic resonance angiography for differentiation between idiopathic and thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: initial results. Eur Radiol 15:2256–2263
Pedersen MR, Fisher MT, van Beek EJ (2006) MR imaging of the pulmonary vasculature-an update. Eur Radiol 16:1374–1386
Rominger MB, Bachmann GF, Pabst W, Rau WS (1999) Right ventricular volumes and ejection fraction with fast cine MR imaging in breath-hold technique: applicability, normal values from 52 volunteers, and evaluation of 325 adult cardiac patients. J Magn Reson Imaging 10:908–918
Lotz J, Meier C, Leppert A, Galanski M (2002) Cardiovascular flow measurement with phase-contrast MR imaging: basic facts and implementation. Radiographics 22:651–671
Glockner JF, Johnston DL, McGee KP (2003) Evaluation of cardiac valvular disease with MR imaging: qualitative and quantitative techniques. Radiographics 23:e9
Mostbeck G, Caputo G, Higgins C (1992) MR measurement of blood flow in the cardiovascular system. AJR Am J Roentgenol 159:453–461
Kondo C, Caputo GR, Semelka R, Foster E, Shimakawa A, Higgins CB (1991) Right and left ventricular stroke volume measurements with velocity-encoded cine MR imaging: in vitro and in vivo validation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 157:9–16
Lee VS, Spritzer CE, Carroll BA, Pool LG, Bernstein MA, Heinle SK, MacFall JR (1997) Flow quantification using fast cine phase-contrast MR imaging, conventional cine phase-contrast MR imaging, and Doppler sonography: in vitro and in vivo validation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 169:1125–1131
Kreitner KF, Ley S, Kauczor HU, Mayer E, Kramm T, Pitton MB, Krummenauer F, Thelen M (2004) Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: pre- and postoperative assessment with breath-hold MR imaging techniques. Radiology 232:535–543
Mousseaux E, Tasu JP, Jolivet O, Simonneau G, Bittoun J, Gaux J-C (1999) Pulmonary arterial resistance: noninvasive measurement with indexes of pulmonary flow estimated at velocity-encoded MR imaging-preliminary experience. Radiology 212:896–902
Laffon E, Laurent F, Bernard V, De Boucaud L, Ducassou D, Marthan R (2001) Noninvasive assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension by MR phase-mapping method. J Appl Physiol 90:2197–2202
Roeleveld RJ, Marcus JT, Boonstra A, Postmus PE, Marques KM, Bronzwaer JG, Vonk-Noordegraaf A (2005) A comparison of noninvasive MRI-based methods of estimating pulmonary artery pressure in pulmonary hypertension. J Magn Reson Imaging 22:67–72
Ley S, Kreitner K-F, Morgenstern I, Thelen M, Kauczor H-U (2002) Bronchopulmonary shunts in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: evaluation by helical CT and MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179:1209–1215
Cheitlin MD, Alpert JS, Armstrong WF, Aurigemma GP, Beller GA, Bierman FZ, Davidson TW, Davis JL, Douglas PS, Gillam LD (1997) ACC/AHA Guidelines for the Clinical Application of Echocardiography. A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee on Clinical Application of Echocardiography). Developed in collaboration with the American Society of Echocardiography. Circulation 95:1686–1744
Himelman RB, Stulbarg M, Kircher B, Lee E, Kee L, Dean NC, Golden J, Wolfe CL, Schiller NB (1989) Noninvasive evaluation of pulmonary artery pressure during exercise by saline-enhanced Doppler echocardiography in chronic pulmonary disease. Circulation 79:863–871
Grünig E, Janssen B, Mereles D, Barth U, Borst MM, Vogt IR, Fischer C, Olschewski H, Kuecherer HF, Kubler W (2000) Abnormal pulmonary artery pressure response in asymptomatic carriers of primary pulmonary hypertension gene. Circulation 102:1145–1150
McGoon M, Gutterman D, Steen V, Barst R, McCrory DC, Fortin TA, Loyd JE (2004) Screening, Early Detection, and diagnosis of pulmonary arterial hypertension: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 126:14S–34S
Prince MR, Alderson PO, Sostman HD (2004) Chronic pulmonary embolism: combining MR angiography with functional assessment. Radiology 232:325–326
Ichikawa Y, Sakuma H, Kitagawa K, Ishida N, Takeda K, Uemura S, Motoyasu M, Nakano T, Nozaki A (2003) Evaluation of left ventricular volumes and ejection fraction using fast steady-state cine MR imaging: comparison with left ventricular angiography. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 5:333–342
van den Hout RJ, Lamb HJ, van den Aardweg JG, Schot R, Steendijk P, van der Wall EE, Bax JJ, de Roos A (2003) Real-time MR imaging of aortic flow: influence of breathing on left ventricular stroke volume in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Radiology 229:513–519
Boxt LM (1996) MR imaging of pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular dysfunction. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 4:307–325
Ley S, Kramm T, Kauczor HU, Mayer E, Heussel CP, Thelen M, Kreitner KF (2003) [Pre- and postoperative assessment of hemodynamics in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension by MR techniques]. Fortschr Röntgenstr 175:1647–1654
Sakuma H, Kawada N, Kubo H, Nishide Y, Takano K, Kato N, Takeda K (2001) Effect of breath holding on blood flow measurement using fast velocity encoded cine MRI. Magn Reson Med 45:346–348
Ley S, Fink C, Puderbach M, Zaporozhan J, Plathow C, Eichinger M, Hosch W, Kreitner KF, Kauczor HU (2006) MRI Measurement of the hemodynamics of the pulmonary and systemic arterial circulation: influence of breathing maneuvers. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:439–444
Arcasoy SM, Christie JD, Ferrari VA, Sutton MS, Zisman DA, Blumenthal NP, Pochettino A, Kotloff RM (2003) Echocardiographic assessment of pulmonary hypertension in patients with advanced lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167:735–740
Tyszka JM, Laidlaw DH, Asa JW, Silverman JM (2000) Three-dimensional, time-resolved (4D) relative pressure mapping using magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 12:321–329
Laffon E, Bernard V, Montaudon M, Marthan R, Barat JL, Laurent F (2001) Tuning of pulmonary arterial circulation evidenced by MR phase mapping in healthy volunteers. J Appl Physiol 90:469–474
Acknowledgement
The authors are very grateful to Mrs. Sandra Kreuscher and Nicola Ehlken for perfectly co-coordinating the patients’ appointments. MRI measurements were excellently performed by Susanne Yubai, RT, and Kathleen Knauer, RT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sebastian Ley and Derliz Mereles: Both authors contributed equally.
This work was supported by the DFG (FOR 474)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ley, S., Mereles, D., Puderbach, M. et al. Value of MR phase-contrast flow measurements for functional assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Radiol 17, 1892–1897 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0559-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0559-9