Abstract
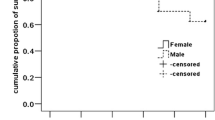
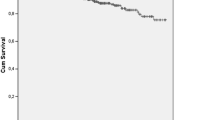
The objective of this study is to determine the causes and predictors of death in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. Causes of death were defined based on death certificates, medical records, and information collected from doctors and relatives. Possible variables predicting mortality were assessed by Kaplan–Meier and Cox regression methods. The multivariate model was validated using the bootstrap method, and the hazard ratios were adjusted according to the shrinkage coefficient. One hundred eighty-one patients were included, and two patients were lost to follow-up. The median (IR) age at T 0 and disease duration of the 179 patients were 26.7 (21.8–34.6) and 8.2 (4.3–12.4) years, respectively. After a median (IR) follow-up of 3.3 (3.1–3.5) years, 13 (7.3 %) patients died due to end-organ failure (5), infection (5), disease activity (1), and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD) (1). The cause of mesenteric ischemia in one patient could not be determined. Predictors of mortality collected at T 0 were the following: nephritis, chronic kidney disease, antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), higher modified SLEDAI-2k, higher damage index score, intravenous cyclophosphamide use, higher daily dose of prednisone, and higher systolic blood pressure. Independent predictors of mortality were higher damage index score (HR: 1.40; 95 % CI: 1.08–1.82), cyclophosphamide use (HR: 3.80; 95 % CI: 1.13–12.77), and APS diagnosis (HR: 3.82; 95 % CI: 1.07–13.59). This paper presents a high frequency of late mortality in lupus patients due to the SLE itself and infection. This result is not in agreement with the initial proposed bimodal pattern of lupus mortality, nor is it in agreement with the high frequency of CVD as a cause of death in developed countries. The most important predictors of death were related to the lupus itself.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borchers AT, Keen CL, Shoenfeld Y et al (2004) Surviving the butterfly and the wolf: mortality trends in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 3:423–453
Cervera R (2006) Systemic lupus erythematosus in Europe at the change of the millennium: lessons from “Euro-Lupus Project”. Autoimmun Rev 5:180–186
Doria A, Iaccarino L, Ghirardello A et al (2006) Long-term prognosis and causes of death in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med 119:700–706
Funauchi M, Shimadzu H, Tamaki C et al (2007) Survival study by organ disorders in 306 Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from a single center. Rheumatol Int 27:243–249
Jacobsen S, Petersen J, Ullman S et al (1999) Mortality and causes of death of 513 Danish patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Rheumatol 28:75–80
Cervera R, Khamashta M, Font J et al (1999) Morbidity and mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus during a 5-year period. A multicenter prospective study of 1,000 patients. European Working Party on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore) 78:167–175
Rabbani MA, Habib HB, Islam M et al (2009) Survival analysis and prognostic indicators of systemic lupus erythematosus in Pakistani patients. Lupus 18:848–855
Tikly M, Navarra SV (2008) Lupus in developing world - is it any different? Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 22:643–655
Bernatsky R, Boivin JF, Joseph L et al (2006) Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 54:2250–2257
Vasoo S, Hughes GRV (2004) Perspectives on the changing face of lupus mortality (edit). Autoimmun Rev 3:415–417
Urowitz MB, Bookman AAM, Koehler BE et al (1976) The bimodal mortality pattern of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med 60:221–225
Rubin L, Urowitz MB, Gladman DD (1985) Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: the bimodal pattern revisited. Q J Med 55:87–98
Moss KE, Ioannou Y, Sultan SM et al (2002) Outcome of a cohort of 300 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus attending a dedicated clinic for over two decades. Ann Rheum Dis 61:409–413
Nossent J, Cikes N, Kiss E et al (2007) Current causes of death in systemic lupus erythematosus in Europe, 2000–2004: relation to disease activity and damage accrual. Lupus 16:309–317
Shinjo SK, Bonfa E, Wojdyla D et al (2010) Antimalarial treatment may have a time-dependent effect on Lupus Survival. Arthritis Rheum 62:855–862
Wadee S, Tikly M, Hopley M (2007) Causes and predictors of death in South Africans with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 46:1487–1491
Telles RW, Lanna CCD, Ferreira GA et al (2007) Frequência de doença cardiovascular aterosclerótica e de seus fatores de risco em pacientes com lúpus eritematoso sistêmico. Rev Bras Reum 47:165–172
Telles RW, Lanna CCD, Ferreira GA et al (2008) Carotid atherosclerotic alterations in systemic lupus erythematosus treated at a Brazilian university setting. Lupus 17:105–113
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of the systemic lupus erythematosus (letter). Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25:1271
Gladman DD, Ibañez D, Urowitz MB (2002) Systemic lupus erythemtosus disease activity index 2000. J Rheumatol 29:288–291
Petri M, Susan G, Barr AZ et al (1999) Patterns of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 42:2682–2688
Gladman DD, Ginzler EM, Goldsmith C et al (1996) The development and initial validation of the systemic lupus international collaborating clinics/American College of Rheumatology damage index for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 39:363–369
Wilson WA, Gharavi AE, Koike T et al (1999) International consensus statement on preliminary classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome—report of an international workshop. Arthritis Rheum 42:1309–1311
Cockcroft D, Gault MK (1976) Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16:31–41
Harrel FE, Lee KL, Mark DB (1996) Multivariable prognostic models: issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat Med 15:361–387
Cardoso CRL, Signorelli FV, Papi JAS et al (2008) Initial and accrued damage as predictors of mortality in Brazilian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a cohort study. Lupus 17:1042–1048
Appenzeller S, Costallat LTL (2004) Análise de sobrevida global e fatores de risco para óbito em 509 pacientes com lúpus eritematoso sistêmico (LES). Rev Bras Reumatol 44:198–205
Alamanos Y, Voulgari PV, Papassava M et al (2003) Survival and mortality rates of systemic lupus erythematosus patients in northwest Greece. Study of a 21-year incidence cohort (letter). Rheumatol 42:1122–1123
Trager J, Ward MM (2001) Mortality and causes of death in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol 13:345–351
Alarcón GS, McGwin-Jr G, Bastian HM et al (2001) Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups. VII. Predictors of early mortality in the LUMINA cohort. Arthritis Rheum 45:1991–2202
Pons-Estel B, Catoggio LJ, Cardiel MH et al (2004) The GLADEL multinational Latin American prospective inception cohort of 1,214 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: ethnic nad disease heterogeneity among “hispanics”. Medicine (Baltimore) 83:1–17
Iriya SM, Capelozzi VL, Calich I et al (2001) Causes of death in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in Sao Paulo, Brazil: a study of 113 autopsies. Arch Intern Med 161:1557
Doria A, Canova M, Tonon M et al (2008) Infections as triggers and complications of systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 8:24–28
Esdaile JM, Abrahamwicz M, Grodzicky T (1998) Myocardial infarction and stroke in SLE: markedly increased incidence after controlling for risk factors. Arthritis Rheum 41:S139
Manzi S, Meilahn EN, Rairie JE et al (1997) Age-specific incidence rates of myocardial infarction and angina in women with systemic lupus erythematosus: comparison with the Framingham study. Am J Epidemiol 145:408–415
Alarcón GS, Roseman JM, McGwin-Jr G et al (2004) Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups. XX. Damage as a predictor of further damage. Rheumatol 43:202–205
Chambers SA, Allen E, Rahman A et al (2009) Damage and mortality in a group of British patients with systemic lupus erythematosus followed up for 10 years. Rheumatol 48:673–675
Rahman P, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB et al (2001) Early damage as measured by the SLICC/ACR damage index is a predictor of mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 10:93–96
Ruiz-Irastorza G, Egurgibe MV, Ugalde J et al (2004) High impact of antiphospholipid syndrome on irreversible organ damage and survival of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Intern Med 164:77–82
Vaarala O (1998) Antiphospholipids antibodies and myocardial infarction. Lupus 7:S132–S134
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Telles, R.W., Lanna, C.C.D., Souza, F.L. et al. Causes and predictors of death in Brazilian lupus patients. Rheumatol Int 33, 467–473 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-012-2372-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-012-2372-x