Abstract
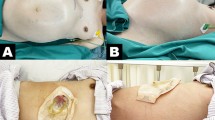
Intestinal pseudo-obstruction (IPO) is not uncommon in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and IPO in SLE has an apparent association with ureterohydronephrosis. However, hepatobiliary dilatation without mechanical obstruction presenting together with IPO and ureterohydronephrosis is much more scarce in SLE. Here, we named this rare triad of IPO, ureterohydronephrosis, and biliary tract dilatation as visceral muscle dysmotility syndrome (VMDS). It always imitates an acute abdomen and is even life-threatening if treated incorrectly. To diagnose a VMDS, infections and mechanical obstructions should be ruled out carefully. Here, we report a 24-year-old Chinese woman with SLE who presented of VMDS that associated with corticoids tapering induced SLE flare. In this case, early vigorous immunosuppressive treatment conquered the triad timely and thus yielded a good outcome.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mok MY, Wong RW, Lau CS (2000) Intestinal pseudo-obstruction in systemic lupus erythematosus: an uncommon but important clinical manifestation. Lupus 9:11–18
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American college of rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
Cacoub P, Benhamou Y, Barbet P, Piette JC, Le Cae A, Chaussade S, Cadranel JF, Callard P, Opolon P, Godeau P (1993) Systemic lupus erythematosus and chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction. J Rheumatol 20:377–381
Park FD, Lee JK, Madduri GD, Ghosh P (2009) Generalized megaviscera of lupus: refractory intestinal pseudo-obstruction, ureterohydronephrosis and megacholedochus. World J Gastroenterol 15:3555–3559
Pardos-Gea J, Ordi-Ros J, Selva A, Perez-Lopez J, Balada E, Vilardell M (2005) Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction associated with biliary tract dilatation in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 14:328–330
Alexopoulou A, Andrianakos A, Dourakis SP (2004) Intestinal pseudo-obstruction and ureterohydronephrosis as the presenting manifestations of relapse in a lupus patient. Lupus 13:954–956
Narvaez J, Perez-Vega C, Castro-Bohorquez FJ, Garcia-Quintana AM, Biosca M, Vilaseca-Momplet J (2003) Intestinal pseudo-obstruction in systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Rheumatol 32:191–195
Nguyen H, Khanna N (2004) Intestinal pseudo-obstruction as a presenting manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus: case report and review of the literature. South Med J 97:186–189
Hill PA, Dwyer KM, Power DA (2000) Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in systemic lupus erythematosus due to intestinal smooth muscle myopathy. Lupus 9:458–463
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y.Q., Xue, Q. & Wang, N.S. Visceral muscle dysmotility syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus: case report and review of the literature. Rheumatol Int 32, 1701–1703 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-1856-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-1856-4