Abstract
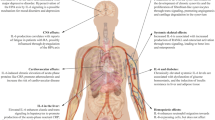
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has severe and lasting effects on quality of life. This review (1) describes the disease progression, disability, and joint destruction that seriously alter a patient’s quality of life, and (2) explains how the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra), anakinra, retards the progress of disease, thereby improving outcomes. Relevant articles were reviewed with a focus on RA, anakinra, and functional and quality-of-life outcomes. In randomized, controlled trials, the IL-1 Ra anakinra provided meaningful benefits for patients with active RA, such as decreased signs and symptoms of disease, slower radiographic disease progression, reduced disability, and improved health-related quality of life. The biologic agent, anakinra, provides to patients with RA a valuable treatment option that has a positive impact on both function and quality of life.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saxne T, Palladino MA Jr, Heinegard D, Talal N, Wollheim FA. Detection of TNF-α but not TNF-β in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid and serum.Arthritis Rheum. 1988; 31: 1041–1045.
Eastgate JA, Symons JA, Wood NC, Grinlinton FM, di Giovine FS, Duff GW. Correlation of plasma IL-1 levels with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis.Lancet. 1988; 2: 706–709.
Tetta C, Camussi G, Modena V, DiVittorio C, Baglioni C. Tumour necrosis factor in serum and synovial fluid of patients with active and severe rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 1990; 49: 665–667.
Shulze-Koops H, Davis LS, Kavanaugh AF, Lipsky PE. Elevated cytokine mRNA levels in the peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis suggest different degrees of myeloid cell activation.Arthritis Rheum. 1997; 40: 639–647.
Arend WP, Welgus HG, Thompson RC, Eisenberg SP. Biological properties of recombinant human monocyte derived IL-1 receptor antagonist.J Clin Invest. 1990; 85: 1694–1697.
Firestein GS, Berger AE, Tracey DE, et al. IL-1Ra protein production and gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis synovium.J Immunol. 1992; 149: 1054–1062.
Koch AE, Kunkel SL, Chensue SW, Haines GK, Strieter RM. Expression of IL-1 and IL-1ra by human rheumatoid synovial macrophages.Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992; 65: 23–29.
Deleuran BW, Chu CQ, Field M, et al. Localization of IL-1α, type 1 IL-1 receptor and IL-1ra in the synovial membrane and cartilage/pannus junction in rheumatoid arthritis.Br J Rheum. 1992; 31: 801–809.
Seckinger P, Klein-Nulend J, Alander C, Thompson RC, Dayer JM, Raisz LG. Natural and recombinant human IL-1 receptor antagonists block the effects of interleukin-1 on bone resorption and prostaglandin production.J Immunol. 1990; 145: 4181–4184.
Firestein GS, Boyle DL, Yu C, et al. Synovial IL-1 receptor antagonist and interleukin-1 balance in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 1994; 37: 644–652.
Scott DL, Pugner K, Kaarela K, et al. The links between joint damage and disability in rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology. 2000; 39: 122–132.
Butt JH, Barthel JS, Moore RA. Clinical spectrum of upper gastrointestinal effects of NSAIDs: natural history, symptomatology and significance.Am J Med. 1988; 84: 5–14.
Corwin HL, Bonventre JV. Renal insufficiency associated with NSAID agents.Am J Kidney Dis. 1984; 4: 147–152.
Spiegel BM, Targownik L, Dulai GS, Gralnek IM. The cost-effectiveness of cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors in the management of chronic arthritis.Ann Intern Med. 2003; 138: 795–806.
Puppo F, Murdaca G, Ghio M, Indiveri F. Emerging biologic drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Autoimmun Ref. 2005; 4: 537–541.
Bresnihan B, Alvaro-Gracia JM, Cobby M, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with recombinant human IL-1ra.Arthritis Rheum. 1998; 41: 2196–2204.
Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, et al. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary core set of disease activity measures for rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. The Committee on Outcomes Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials.Arthritis Rheum. 1993; 36: 729–740.
Paulus HE, Egger MJ, Ward JR, Williams HJ. Analysis of improvement in individual rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs based on findings in patients treated with placebo. The Cooperative Systematic Studies of Rheumatic Diseases Group.Arthritis Rheum. 1990; 33: 477–484.
Cohen S, Hurd E, Cush J, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with anakinra, a recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, in combination with methotrexate: the results of a twenty–four week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46: 614–624.
Kineret® [package insert]. Thousand Oaks, Calif: Amgen Inc; October 2002.
Fries JF, Spitz P, Kraines RG, Holman HR. Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 1980; 23: 137–145.
Pincus T, Sokka T. Quantitative measures and indices to assess rheumatoid arthritis in clinical trials and clinical care.Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2004; 30: 725–751.
Bresnihan B, Cobby M. Clinical and radiological effects of anakinra in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003; 42(suppl 2): ii22-ii28.
Emery P, Woolley JM, Chan WW. Improvement in health-related quality of life from anakinra therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis not using DMARDs [abstract]. Presented at: Annual European Congress of Rheumatology (EULAR 2001); June 16, 2001; Prague, Czech Republic.
Nuki G, Bresnihan B, Bear MB, McCabe D. Long-term safety and maintenance of clinical improvement following treatment with anakinra (recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: extension phase of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46: 2838–2846.
Cohen SB, Woolley JM, Chan WW. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist anakinra improves functional status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2003; 30: 225–231.
Cohen SB, Moreland LW, Cush JJ, et al. A multicentre, double blind, randomized, placebo controlled trial of anakinra (Kineret), a recombinant interleukin 1 receptor antagonist, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with background methotrexate.Ann Rheum Dis. 2004; 63: 1062–1068.
Wells GA, Tugwell P, Kraag GR, Baker PR, Groh J, Redelmeier DA. Minimum important difference between patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the patient’s perspective.J Rheumatol. 1993; 20: 557–560.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kavanaugh, A. Anakinra (Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist) has positive effects on function and quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Therapy 23, 208–217 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02850127
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02850127