Abstract
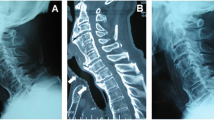
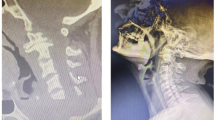
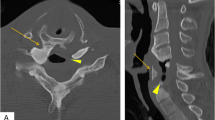
The purpose of our study was to demonstrate the clinical and radiographic findings in patients with dysphagia and ventral osteophytes of the cervical spine due to degeneration or as a typical feature of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH, Forestier Disease). Since 2003 we encountered 20 patients with such changes in the cervical spine causing an impairment of deglutition. A total of 12 patients had one solitary pair of osteophytes of neighboring vertebrae, 4 patients revealed two pairs and 4 patients had triple pairs of osteophytes. Thirty-two osteophytes were observed totally. A total of 14 of these arose from the right, 15 from the left side and 3 from the middle of the anterior face of the vertebra. Ten patients suffered from DISH, while ten patients revealed osteophytes as a part of a degenerative disorder of the cervical spine. The osteophytes had an average length of 19 mm maximum anterior posterior range. Most of the osteophytes (16) were found in the segments C5/6 and C6/7. Osteophytes of vertebrae C3/4/5 occurred in six cases. Only in one case C2/3 was affected. Functional endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) revealed an aspiration of thin liquids in seven patients with osteophytes arising from the anterior face of the vertebra C3/4/5 restricting the motility of the epiglottis, which seemed not to close the aditus laryngis. Retention of solids in the piriform sinus on the side obstructed by an osteophyte (C4/5) could also be repeatedly evidenced through FEES. In one case, a strong impairment of the voice because of an immobility of the right vocal cord due to mechanical obstruction by an osteophyte was the indication for surgical removal of the structure. Thus, the dysphagia of this patient was reduced and his voice turned to normal. The development of symptoms in patients with ventral osteophytes was very much related to the location of the structures. Moreover, the clinical symptoms were to some extent dependent on the size of the osteophytes, although there was no direct correlation between size of the structure and severity of the patient’s complaint.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tiedjen K, Müller KM, Pathologie der degenerativen Wirbelsäulenerkrankungen, Springer-Verlag
Resnick D (1985) Degenerative disease of the vertebral column. Radiology 156:3–14
Kumaresan S, Yoganandan N, Pintar F, Maiman DJ, Goel VK (2001) Contribution of disc degeneration to osteophyte formation in the cervivcal spine: a biomechanical investigation. J Orthop Res 19(5):977–984
Resnick D, Shapiro RF, Wiesner KB, Niwayama G, Utsinger PD, Shaul SR (1978) Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Semin Arthritis Rheum 7:153–187
Resnick D, Niwayama G (1976) Radiographic and pathologic features of spinal involvement in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Radiology 119:559–568
Julkunen H, Heinonen OP, Knekt P, Maatela J (1973) The epidemiology of hyperostosis of the spine together with its symptoms and related mortality in a general population. Scand J Rheumatol 40:581–91
Kiss C, Szilagyi M, Paksy A, Poor G (2002) Risk factors for diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41(1):27–30
Castellano D, Sinacori JT, Karakla DW (2006) Stridor and dysphagia in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Laryngoscope 116(2):341–344
Foglia Fernandez M, Nogues Orpi J, Gonzalez Compta X, Arias Gcuchi G, Dicenta Sousa M (1998) Dysphagia in Forestier`s disease (vertebral ankylosing hyperostosis). Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 49(1):71–4
Ozgocmen S (2005) Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis—induced dysphagia or DISHphagia. APLAR J Rheumatol 8(2):128–130
Akhtar S, O’Flynn PE, Kelly A, Valentine PM (2000) The management of dysphagia in cervical hyperostosis. J Laryngol Otol 114:154–157
Matan AJ, Hsu J, Frederickson BA (2002) Management of respiratory compromise caused by cervical osteophytes: a case report and review of the literature. Spine J 2:456–459
Laus M, Malaguti MC, Alfonso C, Ferrari D, Zapolli FA, Giunti A (1995) Dysphagia due to cervical osteophytosis. Chir Organi Mov 80(3):263–71
Kasper D, Hermichen H, Köster R, Schultz-Coulon H-J (2002) Manifestationsformen der diffusen idiopathischen Skeletthyperostose (M. Forestier) in der HNO-Heilkunde, HNO 2002 50: 978–983
Demuynck K, Van Calenbergh F, Goffin J, Verschakelen J, Demedts M, van de Woijstine K (1995) Upper airway obstruction caused by a cervical osteophyte. Chest 108:283–284
Martin RE, Neary AM, Diamant NE (1997) Dysphagia following anterior cervical spine surgery. Dysphagia 12(1):2–8
Hacki T, Kramer H, Kleinjung Ch, Perez-Alvarez JC, Schmid J (2001) Endoskopische Mehrfarben-Schluckuntersuchung (Endoscopic multicolor investigation of swallowing). Laryngorhinootologie 80:335–340
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seidler, T.O., Pèrez Àlvarez, J.C., Wonneberger, K. et al. Dysphagia caused by ventral osteophytes of the cervical spine: clinical and radiographic findings. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266, 285–291 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-008-0735-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-008-0735-4