Abstract
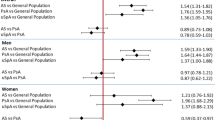
This study evaluated whether people with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and spondyloarthritis are at higher risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We used a sub-dataset of the National Health Insurance Research Database from 1996 to 2010 to established a AS cohort consisting new patients with AS or spondyloarthritis (N = 7,778) and a non-AS cohort without the diseases (N = 31,112). Incidences of T2DM in the two cohorts, hazard ratios (HRs) of risk of T2DM in association with AS, and cumulative probability of having T2DM were estimated by the end of 2010. The incidence of T2DM was 1.17-fold higher in the AS cohort than in the non-AS cohort (13.5 vs. 11.5, per 1,000 person-years), with an adjusted HR of 1.16 (95 % CI = 1.05–1.29). The T2DM incidence was higher for women than for men; while the Cox model measured sex-specific adjusted HR of T2DM was higher for men than for women. The incidence rate of T2DM increased with age in both cohorts, while the age-specific measures showed that the adjusted HR of T2DM was higher in young AS patients (≤50 years of age) than older ones, compared to their peers of non-AS group. The plot of Kaplan–Meier analysis showed that the overall probability of having T2DM was 2 % higher in the AS cohort than in the non-AS cohort (log-rank test: p < 0.0001). Patients with AS and spondyloarthritis have an increased risk of developing T2DM.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ng SC, Liao Z, Yu DT, Chan ES, Zhao L, Gu J (2007) Epidemiology of spondyloarthritis in the People’s Republic of China: review of the literature and commentary. Semin Arthritis Rheum 37:39–47
Akkoc N, Khan MA (2006) Epidemiology of ankylosing spondylitis and related spondyloarthropathies. In: Weisman MHRJ, van der Heijde D (eds) Ankylosing spondylitis and the spondyloarthropathies: a companion to rheumatology. Mosby-Elsevier, London, pp 117–131
Radford EP, Doll R, Smith PG (1977) Mortality among patients with ankylosing spondylitis not given X-ray therapy. N Engl J Med 297:572–576
Lehtinen K (1993) Mortality and causes of death in 398 patients admitted to hospital with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 52:174–176
Mathieu S, Gossec L, Dougados M, Soubrier M (2011) Cardiovascular profile in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 63:557–563
Goodson NJ, Wiles NJ, Lunt M, Barrett EM, Silman AJ, Symmons DP (2002) Mortality in early inflammatory polyarthritis: cardiovascular mortality is increased in seropositive patients. Arthritis Rheum 46:2010–2019
Han C, Robinson DW Jr, Hackett MV, Paramore LC, Fraeman KH, Bala MV (2006) Cardiovascular disease and risk factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 33:2167–2172
Peters MJ, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, Dijkmans BA, Nurmohamed MT (2004) Cardiovascular risk profile of patients with spondylarthropathies, particularly ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 34:585–592
Haffner SM (1999) Epidemiology of insulin resistance and its relation to coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 84:11J–14J
Svenson KL, Lundqvist G, Wide L, Hällgren R (1987) Impaired glucose handling in active rheumatoid arthritis: relationship to the secretion of insulin and counter-regulatory hormones. Metabolism 36:940–943
Svenson KL, Pollare T, Lithell H, Hällgren R (1988) Impaired glucose handling in active rheumatoid arthritis: relationship to peripheral insulin resistance. Metabolism 37:125–130
Ritchie LD, Ganapathy S, Woodward-Lopez G, Gerstein DE, Fleming SE (2003) Prevention of type 2 diabetes in youth: etiology, promising interventions and recommendations. Pediatr Diabetes 4:174–209
Freeman JS (2010) A physiologic and pharmacological basis for implementation of incretin hormones in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mayo Clin Proc 85:S5–S14
Brophy S, Cooksey R, Atkinson M, Zhou SM, Husain MJ, Macey S et al (2012) No increased rate of acute myocardial infarction or stroke among patients with ankylosing spondylitis-a retrospective cohort study using routine data. Semin Arthritis Rheum 42:140–145
Cheng TM (2009) Taiwan’s National Health Insurance system: high value for the dollar. In: Okma KGH, Crivelli L (eds) Six countries, six reform models: the health reform experience of Israel, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Singapore, Switzerland and Taiwan. World Scientific, New Jersey, pp 71–204
Jiang YD, Chang CH, Tai TY, Chen JF, Chuang LM (2012) Incidence and prevalence rates of diabetes mellitus in Taiwan: analysis of the 2000–2009 Nationwide Health Insurance database. J Formos Med Assoc 111:599–604
Ford ES (1999) Body mass index, diabetes, and C-reactive protein among U.S. adults. Diabetes Care 22:1971–1977
McMillan DE (1989) Increased levels of acute-phase serum proteins in diabetes. Metabolism 38:1042–1046
Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A (2002) Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 105:1135–1143
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM (1993) Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 259:87–91
Gimeno RE, Klaman LD (2005) Adipose tissue as an active endocrine organ: recent advances. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:122–128
Hotamisligil GS, Spiegelman BM (1994) Tumor necrosis factor alpha: a key component of the obesity-diabetes link. Diabetes 43:1271–1278
Hotamisligil GS, Murray DL, Choy LN, Spiegelman BM (1994) Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits signaling from the insulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:4854–4858
Brewerton DA, Hart FD, Nicholls A, Caffrey M, James DC, Sturrock RD (1973) Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A 27. Lancet 1:904–907
Schlosstein L, Terasaki PI, Bluestone R, Pearson CM (1973) High association of an HL-A antigen, W27, with ankylosing spondylitis. N Engl J Med 288:704–706
Platz P, Jakobsen BK, Morling N, Ryder LP, Svejgaard A, Thomsen M, Christy M, Kromann H, Benn J, Nerup J, Green A, Hauge M (1981) HLA-D and -DR antigens in genetic analysis of insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 21:108–115
Reitnauer PJ, Roseman JM, Barger BO, Murphy CC, Kirk KA, Acton RT (1981) HLA associations with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in a sample of the American Black population. Tissue Antigens 17:286–293
Pittman WB, Acton RT, Barger BO, Bell DS, Go RC, Murphy CC et al (1982) HLA-A, -B, and -DR associations in type I diabetes mellitus with onset after age forty. Diabetes 31:122–125
Acton RT, Hodge TW, McDaniel DO, Reveille JD, Napier-Littrell M, Barger BO (1985) HLA restriction fragment length polymorphisms associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and the seronegative spondyloarthropathies. Biosci Rep 5:815–829
Sattar MA, Al-Sughyer AA, Siboo R (1988) Coexistence of rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and dermatomyositis in a patient with diabetes mellitus and the associated linked HLA antigens. Br J Rheumatol 27:146–149
Clore JN, Thurby-Hay L (2009) Glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia. Endocr Pract 15:469–474
Mamdani M, Juurlink DN, Lee DS, Rochon PA, Kopp A, Naglie G et al (2004) Cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors versus non-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and congestive heart failure outcomes in elderly patients: a population-based cohort study. Lancet 363:1751–1756
White WB, Kent J, Taylor A, Verburg KM, Lefkowith JB, Whelton A (2002) Effects of celecoxib on ambulatory blood pressure in hypertensive patients on ACE inhibitors. Hypertension 39:929–934
Matthaei S, Stumvoll M, Kellerer M, Häring HU (2000) Pathophysiology and pharmacological treatment of insulin resistance. Endocr Rev 21:585–618
da Silva BS, Bonfá E, de Moraes JC, Saad CG, Ribeiro AC, Gonçalves CR et al (2010) Effects of anti-TNF therapy on glucose metabolism in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis or juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Biologicals 38:567–569
Feldtkeller E, Khan MA, van der Heijde D, van der Linden S, Braun J (2003) Age at disease onset and diagnosis delay in HLA-B27 negative vs. positive patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int 23:61–66
Bakland G, Nossent HC, Gran JT (2005) Incidence and prevalence of ankylosing spondylitis in Northern Norway. Arthritis Rheum 53:850–855
Acknowledgments
The study was supported in part by the study projects (DMR-103-012) in our hospital and Taiwan Department of Health Clinical Trial and Research Center and for Excellence (DOH102-TD-B-111-004), and Taiwan Department of Health Cancer Research Center for Excellence (DOH102-TD-C-111-005).
Conflict of interest
All authors state that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hue-Yong Chen and Hsin-Hung Chen have contributed equally to this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, HH., Yeh, SY., Chen, HY. et al. Ankylosing spondylitis and other inflammatory spondyloarthritis increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in an Asian population. Rheumatol Int 34, 265–270 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2927-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2927-5